When is a drug rash more than just a rash?
You were recently started on antibiotics for an infection and you are now doing well. But slowly your skin begins to itch, and the telltale signs of a rash are already popping up — first on your torso, and now spreading to your arms and legs. What do you do? Should you worry? Should you see a medical professional?
Rashes are a common and pesky side effect of many medications. It can be so disheartening to be getting better from one ailment only to discover that you have another issue to address. While these itchy eruptions can be annoying, they usually run their course over a week or two and can be treated with topical medications.
But not all drug rashes are created equal — and some can even be deadly. Luckily the scary ones are pretty rare, but it's still a good idea to know how to spot them. How can you tell the serious rashes from ones that are just a nuisance, but will get better with time and treatment?
Types of drug rashes
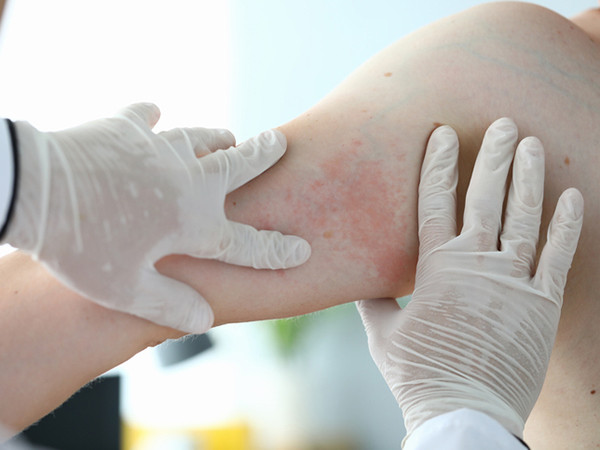
There are two main allergic rashes that may happen after taking a drug. The most immediate type of reaction happens within hours. Hives appear and move around the skin. Since this process is related to the release of histamine, antihistamines (available over the counter at a drugstore) are the typical treatment.
There is also a delayed type of drug rash that comes up four to 14 days after you start taking a medication. Pink and red bumps appear on your chest and back, and spread to the arms and legs over the course of days. Unlike hives, these bumps don't move around, and after a few days things may start to get better, but you may have peeling skin much like a healing sunburn.
This delayed type of rash doesn't respond as well to antihistamines, but an over-the-counter topical cortisone cream (or one of its stronger prescription-strength versions) can help speed the healing process along.
When is a drug rash cause for concern and a visit to the ER?
With hives, the main concern is that you're experiencing a whole-body reaction that goes beyond the skin, one that can make breathing difficult or dangerously drops your blood pressure. If you experience either of these symptoms, it's very important to get to the ED.
These immediate, life-threatening reactions can be treated with steroids, epinephrine, and higher-dose antihistamines than you can find at the drug store. While they are scary, these types of allergic reactions to a drug are not hard to identify, and many doctors are skilled at spotting dramatic changes in your breathing or blood pressure. It's important to tell the doctor you see what medications you have taken and how long ago you took them.
Know the signs of severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs)
In the more delayed type of rash, symptoms can be more difficult to diagnose. The most common triggers for these types of rashes include antibiotics, antiseizure medications, antigout medications like allopurinol, and even over-the-counter medications like NSAIDs. (This isn't a complete list, and any new medication should be regarded with caution.)
As for the rash, when it's just itching things are usually fine, but still a nuisance. When the skin starts to hurt, or turns a deeper purple color, doctors worry about something more serious. If your skin starts to blister up or you see pustules, or if you notice sores in your mouth, eyes, or your genitalia, these are red flags and you should get to an urgent care clinic or the ER and ask for a dermatology consultation. Sores in the mouth can be so severe that drooling becomes a common symptom, because patients avoid swallowing due to the pain.
If you start to feel ill, like you have the flu, or if you're getting puffy from swelling, especially in the face, this could mean it's a severe drug hypersensitivity syndrome. Sometimes people develop a fever, a drop in their blood pressure, or their liver, kidneys, and heart can all be affected by drug hypersensitivity syndromes. These are so severe that most patients need to be admitted to the hospital, and sometimes even to the burn or intensive care unit.
While there are different names for different types of severe drug reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), they are often grouped together as severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs).
What happens if you develop a SCAR from a medication?
The first step is getting evaluated by a specialist, either in a dermatological clinic or the hospital. Finding someone who has expertise in managing these types of reactions is critical. A doctor (usually a dermatologist) may biopsy your skin, and they may have to start systemic medications that suppress your immune system. Sometimes, patients with SCARs also require a stay in a hospital.
The most important thing you can do is to keep an eye on your skin and its symptoms if you're taking a new medication, or even if you've increased the dose of an old medication. If you suspect that you may be dealing with one of these SCARs, be sure to seek help from an expert, like a board-certified dermatologist, so that you can rest assured that you're getting the care you need. Patients who are treated appropriately generally do well. Your doctors should also report these reactions to the FDA.
Once you're on the mend, things can start to get back to normal, but it's important to follow up with your doctors because there are some long-term issues that are important to pay attention to. Ultimately your doctors and healthcare team will advise you on what exactly is safe in the future. Remember that if you're worried about one of these reactions, it's important to stop the medication as soon as possible, but with the input of your doctors.
About the Author

Steven Chen, MD, MPH, Contributor
Disclaimer:
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles.
No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.















