Harvard Health Blog
Read posts from experts at Harvard Health Publishing covering a variety of health topics and perspectives on medical news.
Articles
Addiction: It retrains the brain, is tougher on women
It’s hard for someone who has never battled an addiction to understand how or why a person can’t break free of one. An exchange on the radio about pop star Whitney Houston’s addictions underscores the misconceptions many people have about addiction. Addictions retrain the brain in a way that couples liking something with wanting it. There are important gender differences in addiction. Although men are more likely than women to become addicted to drugs or harmful behaviors, women who have an addiction face tougher challenges.
Sleep helps learning, memory
Sleep may be time off for the body, but it’s part of a day’s work for the brain. During sleep, the brain is hard at work processing the events of the day, sorting and filing, making connections, and even solving problems. New research suggests that dreaming can improve memory, boost performance, and even improve creativity. Naps have been shown to improve recall. Napping won’t make you smart or assure success, but it can help improve your memory and solve problems. Sleeping well at night, and long enough, is associated with good health. The combination is a two-step approach that should give everyone something to sleep on.
The science behind “broken heart syndrome”
Media reports describing “broken heart syndrome” often lump together two completely different conditions. One is stress cardiomyopathy, sometimes known as takotsubo cardiomyopathy. The other is myocardial infarction, better known as a heart attack. A huge sudden stress—like news that a loved one has died, experiencing an earthquake, or learning that your accountant has stolen all of your retirement savings—unleashes a torrent of stress hormones that can trigger one of those conditions. Stress cardiomyopathy is a weakening of the left ventricle, the heart’s main pumping chamber. Over the course of a week or longer, the left ventricle tends to recover its pumping power. Heart attacks occur when something—usually a blood clot—blocks blood flow to part of the heart muscle.
Natural recoverers kick addiction without help
We tend to think that stopping an addictive behavior means joining a group, seeing a therapist, going to a treatment center, or taking a medication that helps with cravings. Some people manage to break an addiction without any help. These “natural recoverers” tend to take two key steps: They find a new hobby, challenge, or relationship to help fill the void left by the addiction. And they start exercising. Exercise is important because it acts as a natural antidepressant. It also prompts the body to release its own psychoactive substances—endorphins—that trigger the brain’s reward pathway and promote a feeling of well-being. Natural recovery isn’t a sure thing, and the more severe the addiction, the harder it is to do.
New anti-lice lotion is good news for nitpickers
ARCHIVED CONTENT: As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date each article was posted or last reviewed. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician. […]
The 11 most expensive medications
Some medications can cost as much as $2,000 a year. But according to a post on the Medical Billing and Coding blog, that’s peanuts. The price tag for a year’s worth of Soliris, a drug used to treat a rare blood disease known as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, is $409,500. The blog lists 10 other drugs that cost $200,000 or more a year. All 11 are so-called orphan drugs, developed specifically to treat rare conditions. The post raises questions about how much is too much when it comes to drug costs. If one of these drugs is keeping you or a family member alive, the sky’s the limit. If not, the cost can seem excessive.
Everyday foods are top 10 sources of sodium
A new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shows that just 10 types of deliver almost half of the average American’s daily sodium. Topping the list are breads and rolls, cold cuts, pizza, poultry, and soups. Almost two-thirds of our daily sodium comes from food bought in stores, and one-quarter comes from food bought in restaurants (which includes fast-food shops and pizza places).The report also showed that Americans take in an average of 3,266 milligrams of sodium a day (about 1½ teaspoons of salt), well above the healthy target of 2,300 milligrams a day. As a nation, cutting back on salt by an average of 400 milligrams a day could prevent 28,000 deaths a year and save $7 billion in health care costs.
Switching to generic Lipitor
Lipitor, the blockbuster cholesterol-lowering drug, is now being sold as a less-expensive generic. Several other best-selling prescription drugs are set to lose patent protection this year, including Actos, a diabetes drug; Plavix, which helps prevent heart attacks and strokes; and Singulair, an important asthma drug. Although the lower price is great, some people worry that changing from a brand-name drugs to a “no-name” generic one might be risky. Not so, says Dr. Anthony Komaroff, editor in chief of the Harvard Health Letter. In the newsletter’s February 2012 issue, he tackles the brand-versus-generic issue. The FDA is legally required to determine that generic products are “bioequivalent” to brand-name drugs, which means that they produce similar blood concentrations of the same chemical. The vast majority of studies show that generic versions are just as safe and effective as their brand-name counterparts.
FDA needs stronger rules to ensure the safety of dietary supplements
Back in 1994, the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) allowed companies to sell dietary supplements with established ingredients (meaning those that had been sold in the United States before 1994) without any evidence that they are effective or safe. Manufacturers are supposed to give the FDA evidence that a new ingredient should be safe, but this aspect of the law hasn’t been enforced, writes Harvard Medical School’s Dr. Pieter A. Cohen in a commentary in the New England Journal of Medicine. Compare this hands-off approach with the strict rules and regulations for drugs. Last July, the FDA proposed some rules to help it test new dietary supplements. This is a good first step, but the FDA’s plan doesn’t go far enough, argues Dr. Cohen.
Anorexia, bulimia, and other eating disorders in midlife and beyond
Eating disorders don’t afflict only adolescents and young women, but plague older women, too, and may be shrouded in even greater shame and secrecy. Many women don’t seek help, especially if they fear being forced to gain weight or stigmatized as having a “teenager’s disease.” As reported in the February 2012 Harvard Women’s Health Watch, clinicians are reporting an upswing in requests from older women for help with eating disorders. For some of these women, the problem is new; others have struggled with anorexia, bulimia, binge eating, or another eating disorder for decades. Eating problems at midlife and beyond stem from a variety of causes, ranging from grief and divorce to illness, shifting priorities, and heightened awareness of an aging body.
Heart’s “fountain of youth” starts flowing early
If you want to have a healthy heart in your senior years, take care of it while you’re young. In a large study, researchers from Northwestern University found that a 45-year-old man who had normal blood pressure and cholesterol levels, who didn’t smoke, and who didn’t have diabetes had just a 1.4% chance of having a heart attack or stroke during the rest of his life. Having one major risk factor boosted the risk 20-fold. The results were similar for men and women, blacks and whites. Lead researcher Donald Lloyd-Jones said that making it to middle age with no heart disease risk factors is like “the fountain of youth for your heart.”
Doctors debate use of email for communicating with their patients
Among doctors, there is some controversy over whether or not to use email to communicate with patients. The Wall Street Journal offered a peek into the controversy by asking two prominent doctors to write about why they do, and don’t, use email to communicate with their patients. Writing in favor of email was Dr. Joseph C. Kvedar, a dermatologist and founder of the Center for Connected Health, a Harvard-affiliated organization that aims to move health care from the hospital and doctor’s office into the day-to-day lives of people who need help. Taking the opposite side was Dr. Sam Bierstock, an ophthalmologist who is now the president of Champions in Healthcare, an information technology consulting group. Both doctors make good points making me think that, at least for a while, the use of email will probably come down to personal preference, for doctors and the rest of us.
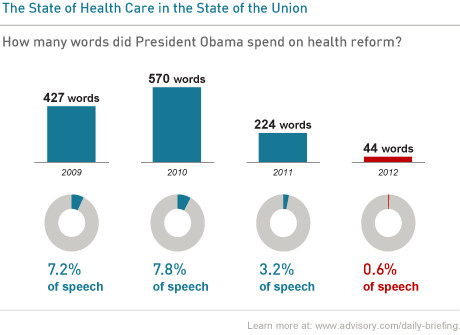
Health care largely ignored in State of the Union address
During last night’s State of the Union address, President Obama spent just 44 words on health reform. That’s far fewer than he’s used in the past. Although health care reform may not be a hot issue right now, it is still something that affects us all. What would you have wanted President Obama to have said about it in the State of the Union address?
Smokers with cancer benefit from quitting, but need extra help
Many people have trouble quitting smoking even after learning they have cancer, according to a new study from Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital. Five months after learning they had cancer, just over one-third (37%) of smokers diagnosed with lung cancer and two-thirds (66%) of those with colorectal cancer were still smoking. The results underscore how difficult it can be to quit smoking. A diagnosis of cancer can be a powerful motivator, but it isn’t always enough—extra help is often needed to quit. Kicking a smoking habit is good for health anytime. It is even more important after a diagnosis of cancer.
Older women may need fewer bone tests
The bone-thinning condition known as osteoporosis can be a big problem for older people. That’s why older folks are urged to have their bones checked with a test that measures bone density. Exactly how often to have the test hasn’t yet been set. By following 5,000 older women for almost 17 years, researchers found that the timing of the next bone mineral test should depend on the result of the current one. People who get a normal result can wait 15 years, those with moderate osteopenia should have the test every five years, while those with severe osteopenia should have it every year.
National plan aims to bolster fight against Alzheimer’s
By the year 2050, experts estimate that 16 million Americans will be living with this Alzheimer’s disease. In an effort to head off the explosion, President Obama has signed into law the National Alzheimer’s Project Act. This ambitious project aims to attack Alzheimer’s disease by improving early diagnosis, finding effective prevention and treatment strategies, providing better support for family caregivers, and more. A newly released draft of the project, which a panel of experts is reviewing this week, sets a 2025 deadline for achieving these and other goals. One big drawback—the act doesn’t provide concrete details about how to fund the research and implementation efforts needed to meet the goals.
When are obsessions and compulsions in children a problem?
It is normal for children at some points in their development to be concerned about sameness and symmetry and having things perfect. But when such beliefs or behaviors become all-consuming and start interfering with school, home life, or recreational activities, the problem may be obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Obsessions are irrational thoughts, images, and impulses that a person feels as unrealistic, intrusive, and unwanted. To relieve the anxiety caused by these obsessions, a youth may engage in compulsive rituals. Two main types of treatment are used to help youths better manage OCD: a form of talk therapy known as cognitive behavioral therapy, and medication. The ideal approach is to try cognitive behavioral therapy before turning to medication.
Let’s protect a million hearts—including yours
A bold initiative called Million Hearts aims to prevent one million heart attacks and strokes from happening over the next five years. As explained in the Harvard Heart Letter, the initiative is spearheaded by the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Its main focus is to encourage more widespread and appropriate use of simple, effective, and inexpensive heart-protecting actions, dubbed the ABCS. These include taking daily low-dose Aspirin, if prescribed; managing Blood pressure and Cholesterol levels; quitting Smoking. The Harvard Heart Letter adds D for Diet and E for Exercise.
Chefs, nutrition experts give the low-fat muffin a makeover
Most store-bought muffins deliver the same wallop of highly processed flour and sugar as donuts. Low-fat versions may actually be worse, since they contain extra sugar and salt. To restore the muffin to its rightful place as a healthy breakfast or snack option, chefs and dietitians from the Culinary Institute of America worked on a muffin makeover with nutrition experts from the Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH). They created recipes for five muffins: blueberry, cranberry orange, jalapeno cheddar corn, lemon chickpea, and banana nut. The team replaced half of the white flour with whole wheat or other whole-grain flours, used heart-healthy oils in place of some or all of the butter, added nuts when possible, and cut the size of the muffins.
Limiting antibiotic use in farm animals will help reduce antibiotic resistance
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has ruled that farmers must limit the use of antibiotics called cephalosporins to prevent infections in seemingly healthy cows, pigs, chicken, and turkeys. According to the FDA, 24.6 million pounds of antibiotics are used each year in cattle, pigs, chickens, and turkeys purely for the sake of prevention. This practice has contributed to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which are a growing threat to human health. Doctors often prescribe cephalosporins to stop common infections such as pneumonia and urinary tract infections. They are also used before surgery. Unfortunately, more and more infections are resistant to cephalosporins. Doctors are being asked to prescribe antibiotics only when they are most needed. Farmers should do the same thing. Otherwise, antibiotics lose their power. Bacteria strains become drug-resistant. And people suffer.

Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up