Alcohol and fatigue
Sedative effects of drinking can also initiate other physical responses in the body
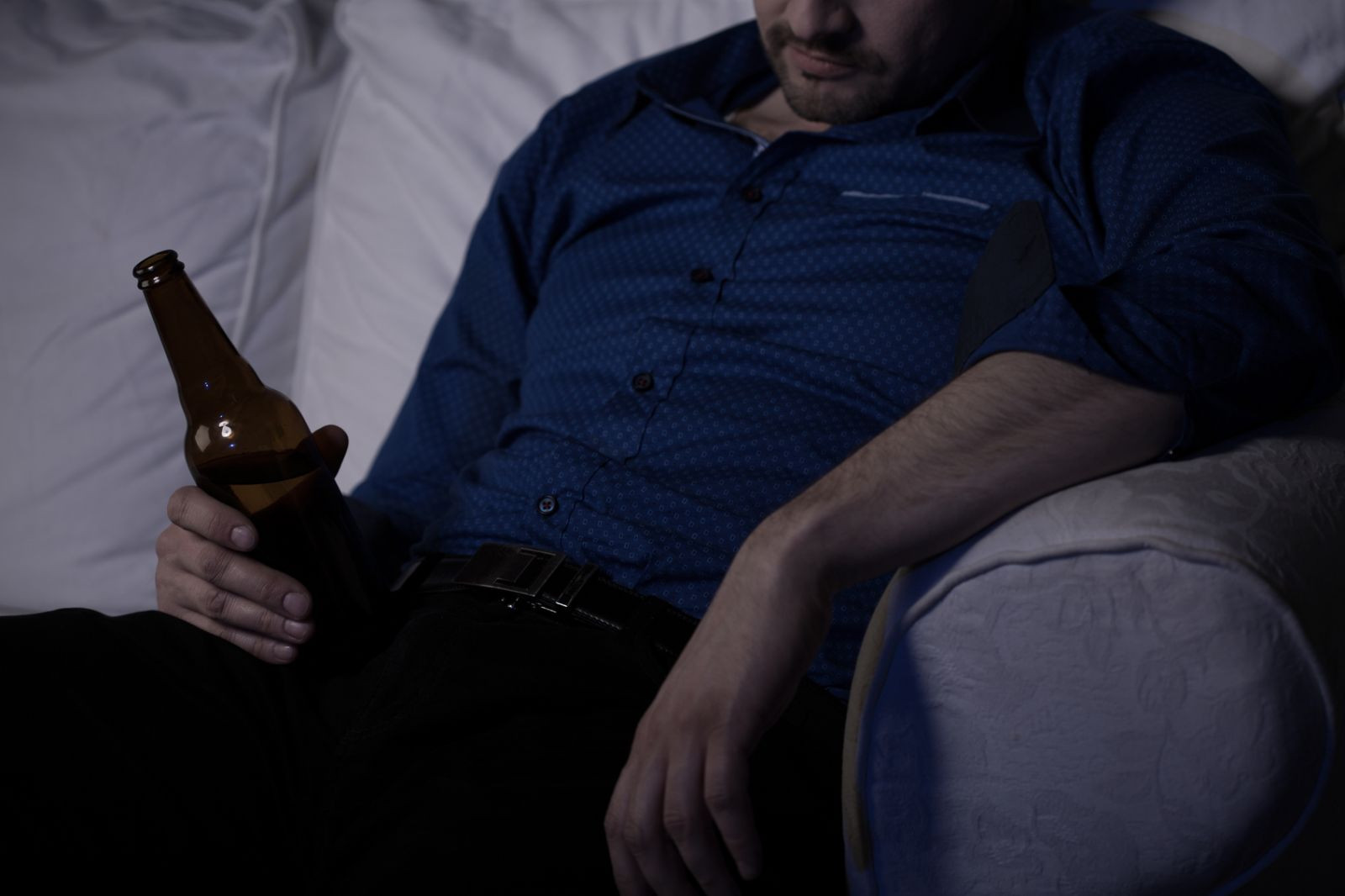

Image: KatarzynaBialasiewicz/Thinkstock
Many people think that a little nightcap will help them sleep soundly through the night. Although alcohol's sedative effects can make you drowsy, they also have other effects that can interfere with quality sleep.
Several hours after that nightcap, the alcohol raises the body's level of epinephrine, a stress hormone that increases the heart rate and generally stimulates the body, which can result in nighttime awakenings. Indeed, alcohol may account for 10% of cases of persistent insomnia. Alcohol also relaxes throat muscles, and this relaxation can worsen sleep-related breathing problems and contribute to sleep apnea. What's more, alcohol may increase the need to urinate during the night — just another way in which it can disrupt sleep.
Alcohol's sedative quality can rob you of energy in another way. Drinking wine, beer, or hard liquor during the day can make you feel drowsy or lethargic. If you didn't sleep well the night before, even one drink can make you drowsy, especially if you drink during one of your usual low-energy times — for example, midafternoon or late evening.
How do you fight fatigue naturally?
One beverage that can boost your energy is plain old water. One of the first signs of being short on fluids is a feeling of fatigue and weakness. Approximately 50% to 60% of your body weight is water, and you are constantly losing water through urine, sweat, and breathing. This water needs to be replenished. Consuming a sufficient amount of fluids in beverages and water-filled foods (such as fruits, vegetables, and soup) will help you maintain your energy.
To learn more about an energy-boosting lifestyle, buy Boosting Your Energy, a Special Health Report from Harvard Medical School.
Disclaimer:
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles.
No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.