Protein intake associated with less cognitive decline
News briefs
- Reviewed by Anthony L. Komaroff, MD, Editor in Chief, Harvard Health Letter; Editorial Advisory Board Member, Harvard Health Publishing
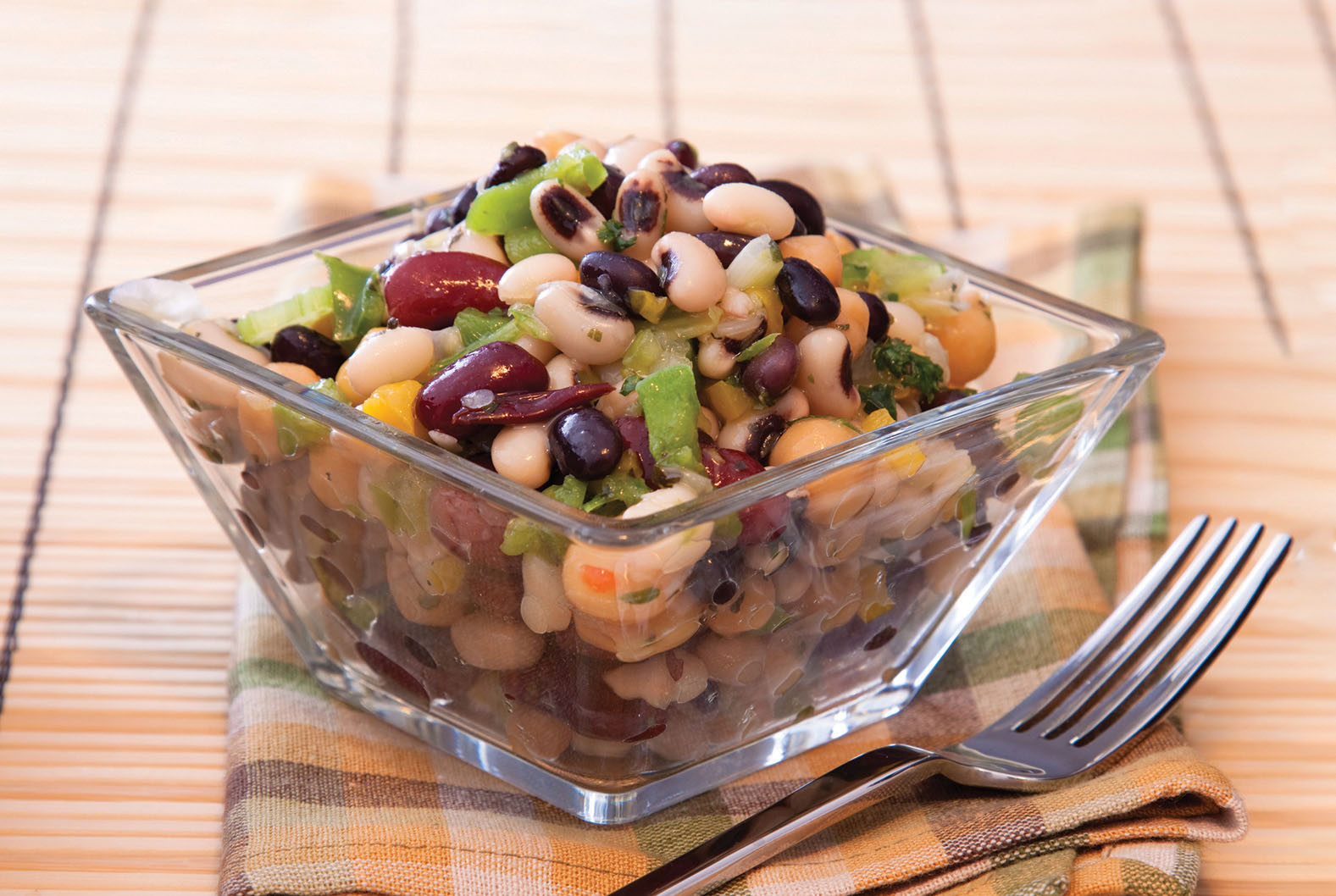

A Harvard study published in the January 2022 issue of The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggests that getting enough protein in your diet may be important for protecting your cognition. Researchers evaluated the self-reported dietary habits and health of more than 77,000 men and women who were followed for more than 20 years. Compared with eating carbohydrates, eating protein was associated with lower odds of developing cognitive decline later in life. It didn't take much to make a difference. For example, for every 5% of calories that came from animal protein instead of carbohydrates, there was an 11% lower risk for developing dementia. And for every 5% of calories that came from plant protein instead of carbohydrates, there was a 26% lower risk for developing dementia. "Beans and legumes had the strongest protective association. Peas and lima beans in particular were associated with a 28% lower risk of cognitive decline for every additional three servings per week," says Dr. Tian-Shin Yeh, the lead author and a postdoctoral research fellow at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The study was observational and doesn't prove that eating more protein will protect your brain. But we already know that proteins are the building blocks of muscles and organs and are essential for tissue and cell repair and the production of important brain chemicals. So be sure to add proteins to your plate at each meal, especially plant-based proteins such as beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds.
Image: © graytown/Getty Images
About the Author

Heidi Godman, Managing Director
About the Reviewer

Anthony L. Komaroff, MD, Editor in Chief, Harvard Health Letter; Editorial Advisory Board Member, Harvard Health Publishing
Disclaimer:
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles.
No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.