Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve

VO2 max: What it is and how you can improve it
Allergies Archive
Articles
How can I know if my penicillin allergy is real?
People who are allergic to penicillin are often given less effective medications that can make them more susceptible to infections, but many people who believe they are allergic to penicillin are not. New techniques are allowing medical providers to assess whether or not a person has a true penicillin allergy.
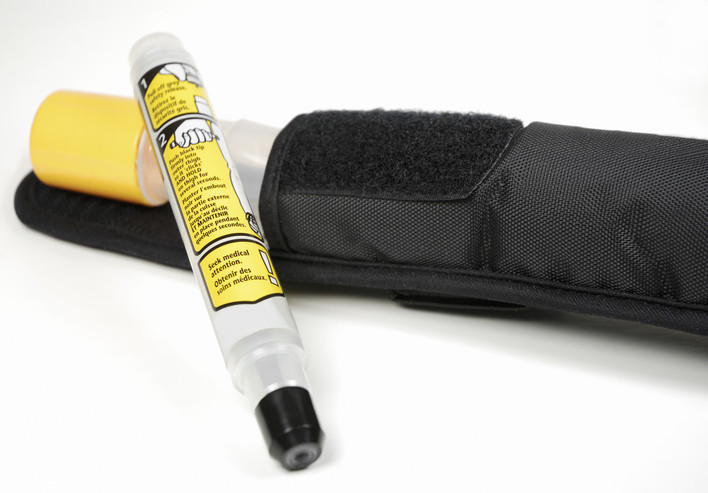
Epinephrine is the only effective treatment for anaphylaxis
Many people have experienced mild allergic reactions to a food, medication, or other allergen, but a severe reaction can be harmful or even fatal. Anaphylaxis must be treated with epinephrine as quickly as possible, followed by a visit to a hospital emergency room for observation.
4 "must dos" for kids with seasonal allergies
Many children look forward to warm, mild spring weather, but kids with seasonal allergies (also known as hay fever) might not. Hay fever can interfere with a child's ability to play outdoors, and it can just plain make them feel miserable. These tips can help your child cope with allergy season — and they work just as well for adults, too.
Think your baby is allergic to cow’s milk?
Babies who show certain digestive symptoms may be incorrectly diagnosed with cow’s milk allergy and put on special diets, although this allergy is uncommon.
Two common prescription drugs now available over the counter
News briefs
On Feb. 14, 2020, the FDA announced that two popular symptom-relief drugs can now be sold without a doctor's prescription. One is diclofenac sodium topical gel, 1% (Voltaren Arthritis Pain), which is used to temporarily relieve arthritis. The other is olopatadine (Pataday), which comes in eye drop form (in two strengths, for once-a-day or twice-a-day dosing) to relive itchy or red eyes from pollen, ragweed, grass, or animal hair or dander. Even though these medications are now available over the counter, they still have risks and benefits, so talk to your doctor before using any new treatment.
Image: MJ_Prototype/Getty Images
Allergic rhinitis: Your nose knows
Allergic rhinitis, commonly called hay fever, can be a minor seasonal nuisance or a troubling year-round problem. Most people can find relief by taking an antihistamine and by avoiding the allergens that trigger the irritation.
Peanut allergy: A new medicine for children may offer protection
In children with food allergies, peanut allergy is the one most likely to cause a severe reaction. A newly approved medication made from peanut flour treats peanut allergy by giving a gradually increasing dosage over several months.
Food allergy, intolerance, or sensitivity: What’s the difference, and why does it matter?
Many people have experienced unpleasant symptoms related to food, but such a reaction does not necessarily mean that you have a food allergy. The symptoms could indicate a food intolerance, food sensitivity, or possibly celiac disease.
Eosinophilic esophagitis: A new food-related allergic condition on the rise?
Eosinophilic esophagitis is an allergic inflammation of the esophagus that most typically develops as an allergic response to certain foods. The exact cause is unclear, but if left untreated it can lead to permanent scarring or narrowing of the esophagus.
How can I reduce symptoms from my winter allergies?
Ask the doctors
Q. I have terrible allergies every winter. What can I do to make them more tolerable this year?
A. Unlike fall or spring allergies, which are often responses to outdoor allergens, such as pollen or ragweed, most winter allergies are triggered by substances inside your home. Common indoor allergens include dust mites, mold, and pet dander, and they can prompt a host of symptoms, from a runny nose and sneezing to a sore throat and itchy eyes. While these indoor allergens are present year-round, allergies can flare up in the winter because you're cooped up in the house with the windows closed. Your home's furnace may also be circulating these substances through the air once the heat kicks on.

Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve

VO2 max: What it is and how you can improve it
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up