Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine
Alternative & Integrative Health Archive
Articles
How the placebo effect may help you
There is growing evidence that the placebo effect is at work in most successful medical therapies.
Image: © BakiBG/Thinkstock
When you were a child, your mother or grandmother might have used a home remedy that made you feel better, especially when it was delivered with a soothing hand on the forehead or a kiss on the cheek. Perhaps she assured you that a cup of warm milk would help you fall asleep, and you found that it did.
Unbeknownst to you — or her — she was probably harnessing the placebo effect, loosely defined as a favorable response to a medical intervention that doesn't have a direct physiological effect. Although you may have learned later in life that there isn't much scientific evidence to support the practice, you may still sleep better after a cup of warm milk at bedtime.
Ask the doctor: Should I take a probiotic?
It’s unclear why, but it appears that people with psoriasis are more likely to also suffer from diabetes.
Bed rest for back pain? A little bit will do you.
Bed rest, once a key part of treating back pain, has a limited role in healing sore backs. In very small doses, bed rest can give you a break when standing or sitting causes severe pain. Too much may make back pain worse. Here is how to do bed rest "right."
To get the most from staying in bed, limit the time you are lying down to a few hours at a stretch, and for no longer than a day or two. You can rest on a bed or sofa, in any comfortable position. To ease the strain on your back, try putting pillows under your head and between your knees when lying on your side, under your knees when lying on your back, or under your hips when lying on your stomach. These positions reduce forces that sitting or standing impose on the back — especially on the discs, ligaments, and muscles.
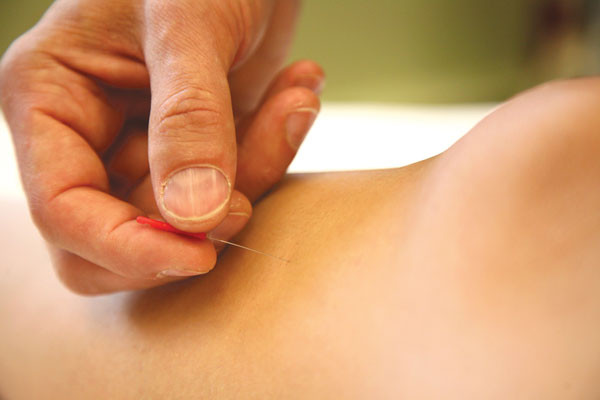
Electroacupuncture may ease hot flashes, aid sleep in breast cancer survivors
Electroacupuncture may be an effective alternative to medication for relieving hot flashes causing sleep disturbances in postmenopausal women.
Modern acupuncture linked to constipation relief
It appears that electroacupuncture may be a treatment option for people with chronic severe functional constipation.
The healing power of touch
Massage therapy can help relieve pain, speed recovery from injury or surgery, and reduce stress.
Image: Jacob Wackerhausen /Thinkstock
Men may think of massage as an occasional treat or a vacation indulgence, but this type of therapy could be a natural way to stay healthy and pain-free.
One of the most common health issues for older men is chronic pain, defined as pain that lasts more than 12 weeks. This includes back pain, headache, cancer pain, and arthritis pain. Then there are the everyday aches from daily living. All of these act as barriers to a healthy lifestyle.
Does cranberry extract prevent UTIs?
Scientific evidence doesn’t support taking cranberry extract to prevent urinary tract infections.
Body scan mindfulness exercise for pain
Stress reduction expert Jon Kabat-Zinn recommends the body scan mindfulness exercise as the best form of mindfulness meditation for pain conditions.
He advises practicing it every day for 45 minutes, even if it seems boring or doesn't seem to be helping. "You don't have to like it, you just have to do it," he explains in his book. "Whether you find the body scan to be very relaxing and interesting or difficult and uncomfortable or exasperating is irrelevant to whether it will serve you well." The goal of the body scan is not to relieve the pain completely, but to get to know it and learn from it so you can manage it.
Treating pain with your brain
Mindfulness can be an effective adjunct to medication for chronic pain.
Image: Tetmc/ Thinkstock
For a long time, people with chronic pain have had to make a trade-off—enduring the discomfort stoically or taking medications that pose additional health risks, including dependence and addiction. But in the last few years, medicine has added another approach that has no troubling side effects: mindfulness.
"Mindfulness is basically paying attention to the present moment without judging," says Dr. Sara Lazar, a neurologist at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital. It is a component of many relaxation techniques, including yoga, deep breathing, tai chi, massage, reflexology, journaling, and prayer.

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up