Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Back Pain Archive
Articles
Pain and neuromodulation: What’s all the “buzz” about?
Neuromodulation therapies use a targeted stimulus to help people manage pain. This can be in the form of an electrical stimulation device or a pump containing medication, either of which can be implanted in the body.
Straight talk on planking
Your core muscles are your body’s foundation, and the plank pose is a great exercise to do to help build core strength—it’s challenging but not complicated. Here’s everything you need to know to plank correctly.
When do I need an imaging test for my back pain?
On call
Q. I suddenly developed low back pain for the first time. My doctor said I did not need an x-ray or other imaging test. Is that normal and are there any situations when a test would be needed?
A. Yes, your doctor is following the current guidelines. Unless you have other symptoms in addition to low back pain, an x-ray, CT scan, or MRI is not likely to be helpful. But it could cause unnecessary worry while waiting for the results and cost you some money if it's not covered by your health insurance. In addition, many people have "false-positive" results in which an abnormality is detected but turns out to be harmless.
When to get help for low back pain
Image: Thinkstock |
Pain from ruptured discs and arthritis doesn't have to flatten you. There are a variety of ways to ease lower back pain discomfort and reduce disability, often without drugs.
Spinal problems are the price we pay for walking upright. Wear and tear on our backbones and the constant pull of gravity on our vertebrae take their toll over time. Nearly every adult has had a stiff or sore back at some time.
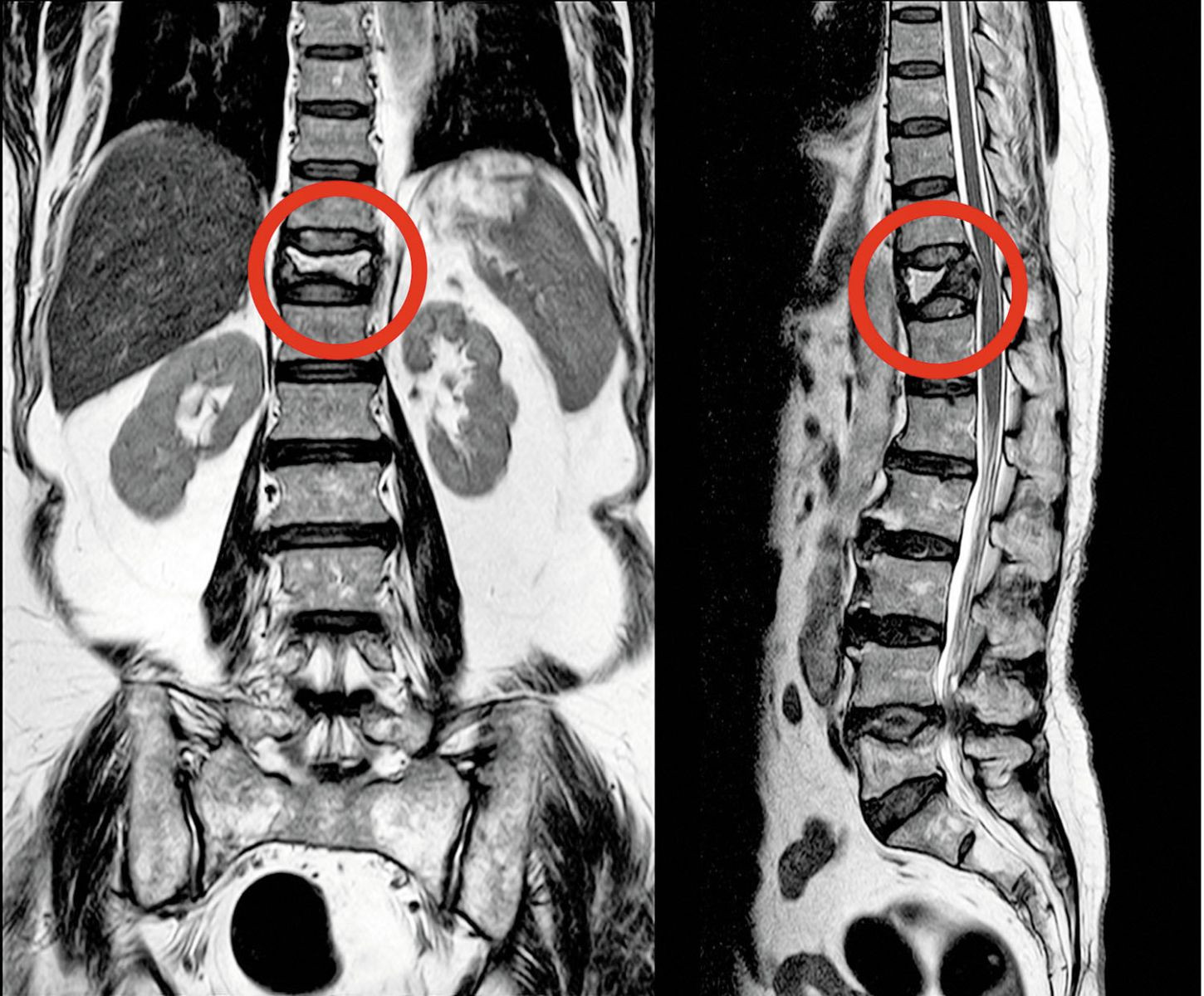
A broken back without the fall
Don't ignore back pain, height loss, or osteoporosis. They could be signs of a compression fracture.
You didn't fall, and you didn't do anything strenuous. So it may come as a surprise when the bad back pain you've been experiencing turns out to be one or more broken bones in your back. "A common story is that someone bends down to put something in the dishwasher or steps off a curb a little hard and puts additional load on their spine. The weakened bone is not adequate to take that load, and it collapses," says Dr. Julia Charles, a rheumatologist and bone cell researcher at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
What weakens the spine?
Your spine contains about 30 bones called vertebrae, stacked on top of each other like a roll of quarters. Each vertebra consists of an external bone surface (like plaster), and an inside filled with a honeycomb of support rods called trabeculae.
I’m in pain, so why is my doctor suggesting a psychologist?
The negative emotions that come from coping with chronic pain can lead to depression, and that very depression can lead to worse pain. Understanding the connection between pain and emotional health with the help of a psychologist can address these issues, and there are evidence-based therapies that can help as well.
Rubbing it in
Pain relief creams and ointments can get the medicine right to where it hurts, and the smell is often familiar and soothing. But do they work?
When something like a knee hurts, there's a natural tendency to rub it. And if it really hurts, most of us will think about popping a pain-relieving pill of some kind — acetaminophen (Tylenol) for starters, or perhaps one of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn).
By the way, doctor: What can I do about ischial bursitis?
Q. I have a pain in my right buttock, which my doctor says is ischial bursitis. Is there anything I can do for the pain or to make the condition go away?
A. Ischial bursitis, sometimes called ischiogluteal bursitis, is an inflammation of the fluid-filled sac, or bursa that lies between the ischial tuberosity (the lower part of the V-shaped bone that helps form the pelvis) and the tendon that attaches the hamstring muscle to the bone. It helps to understand the location of the ischial bursa is by recognizing that it’s the part of your body that bears most of the pressure when sitting in a saddle. Injury or overuse can cause the bursa to become inflamed, swollen, and painful — a condition called bursitis. Ischial bursitis can result from sitting for long periods on a hard surface, from direct trauma to the area, or from injury to the hamstring muscle or tendon through activities such as running or bicycling.

Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up