5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Controlling Your Blood Pressure Archive
Articles
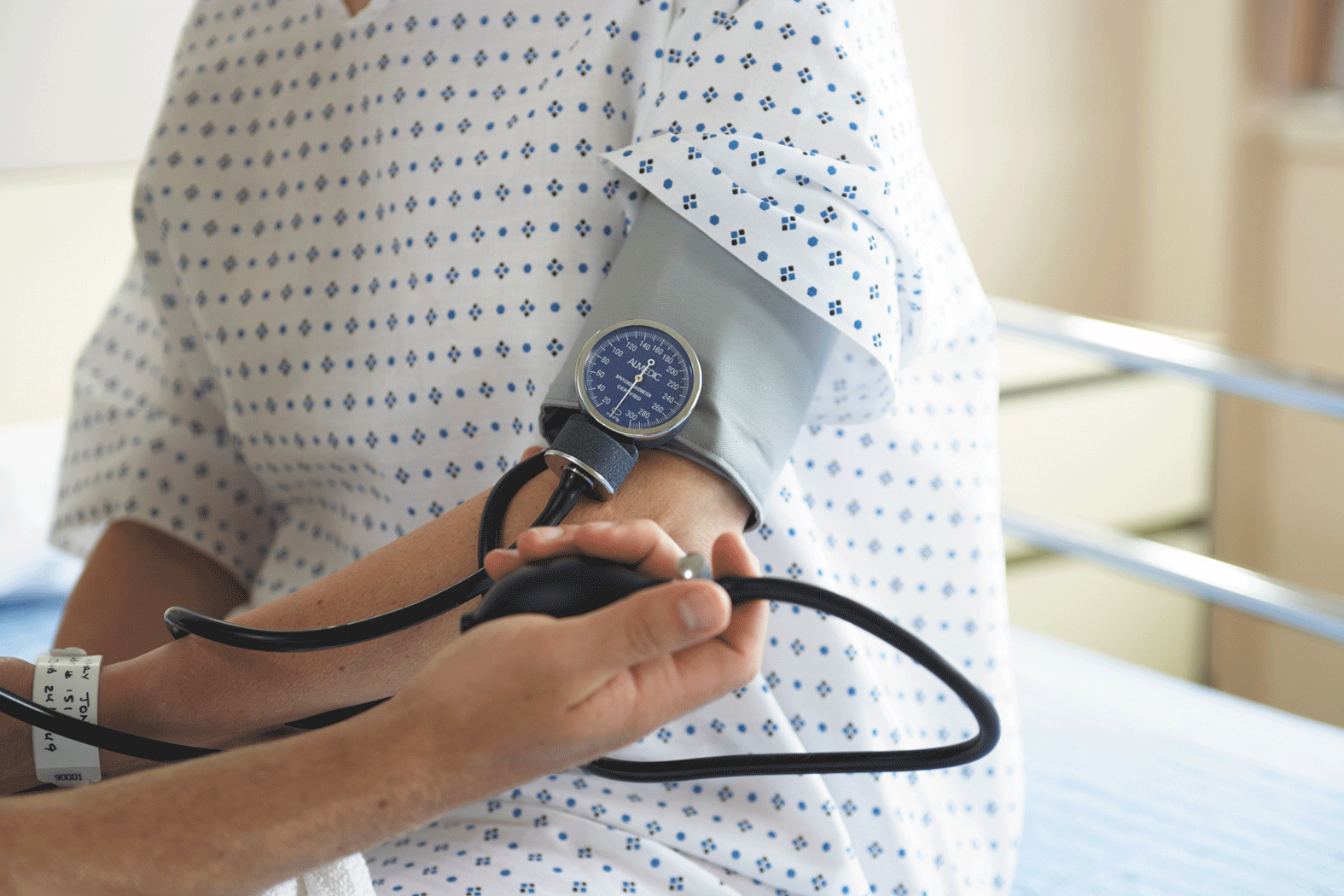
How to determine— and achieve—your target blood pressure
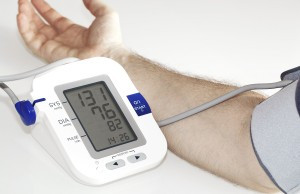
Take an active role by checking your blood pressure with a home monitor.
Most appointments with a health care provider begin with a gentle squeeze—the sensation of a blood pressure cuff inflating around your upper arm. But that single blood pressure reading offers only a glimpse of the health of your cardiovascular system.
"When you have your blood pressure checked in the doctor's office, you're in an artificial environment that is not reflective of the vast majority of the time when your blood pressure is going through its daily excursions," says cardiologist Dr. Elliott Antman, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. Throughout the course of a day, the average person's systolic b-lood pressure (the first number in the reading) may fluctuate considerably.
Do you need a cardiologist?
Your primary care provider should help you control risks for heart disease and refer you to a cardiologist if needed.
Any primary care provider you see—a doctor, nurse practitioner, or physician's assistant—should offer detailed advice on how to lessen your odds of cardiovascular disease, which is responsible for one in three deaths in the United States. However, some people need more specialized care for their hearts.
"I see or hear from a lot of people who have very common problems, like high cholesterol and high blood pressure, who think they need to see a cardiologist," says Dr. Patrick O'Gara, a cardiologist at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. For many people, a primary care physician can effectively manage those problems. But if you have specific concerns, talk to your doctor about whether more specialized care might be beneficial, says Dr. O'Gara.
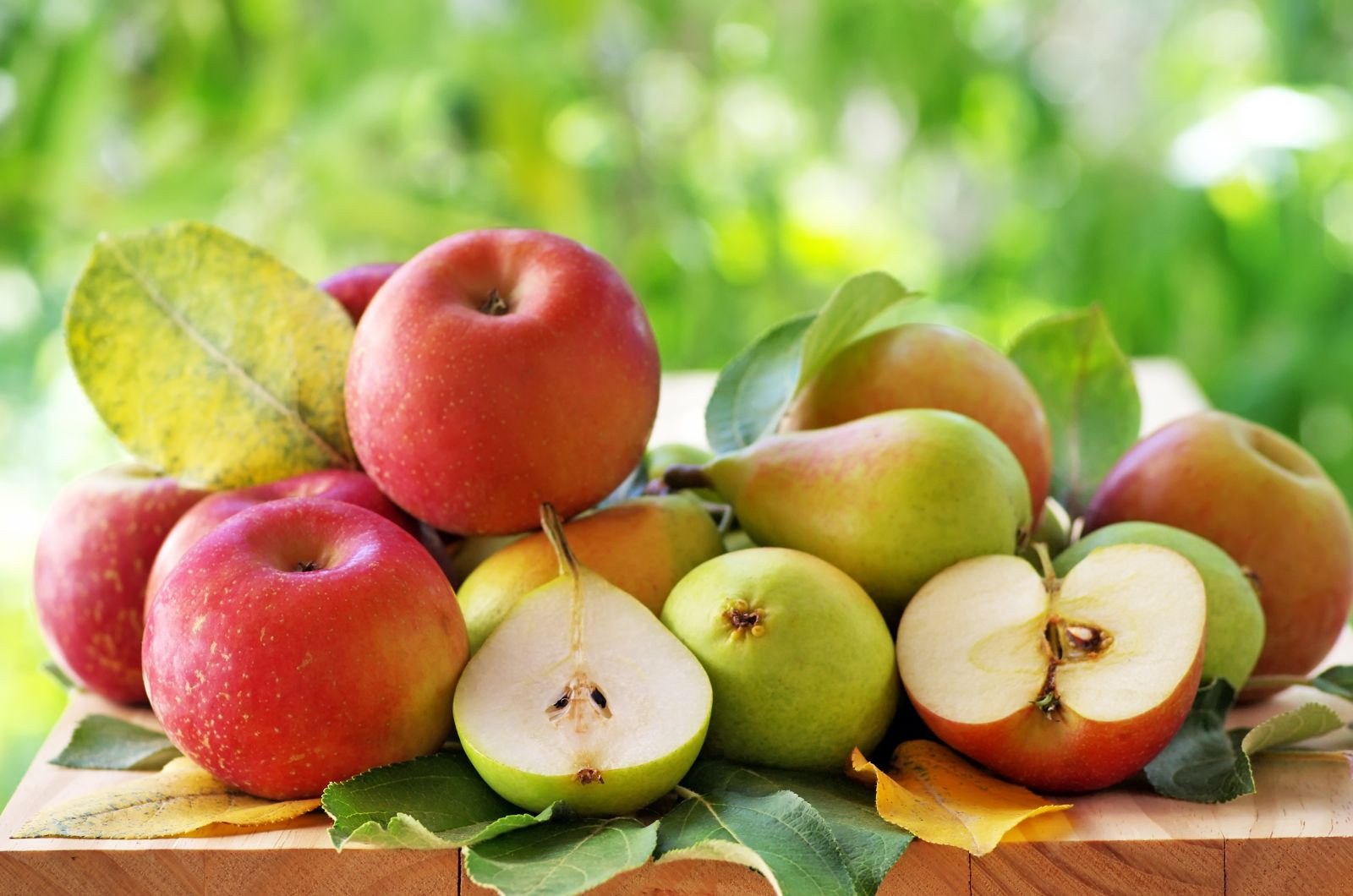
Eating more fruit may help lower blood pressure
The longstanding "More Matters" campaign urges Americans to eat more fruits and vegetables (see www.fruitsandveggiesmorematters.org). Evidence to support this healthy habit keeps piling up, with the latest from a study that pooled dietary data from three large, long-term studies that followed more than 187,000 people for an average of over 20 years.
The researchers found that people who ate more whole fruits—especially apples, pears, grapes, and raisins—were less likely to develop high blood pressure than those who rarely ate those foods. As for vegetables, broccoli and carrots appeared to be the best choices for staving off high blood pressure. Fruits and vegetables provide minerals such as potassium and substances called flavonoids, both of which are linked to lower blood pressure. The study was published online in the Dec. 7, 2015, issue of Hypertension.
Stronger hands linked to a healthier heart
The strength of your hands may hold clues to the health of your heart. A study in the December 2015 American Journal of Preventive Medicine found that people with stronger handgrips had more favorable findings on measures of their cardiovascular health than those with weaker grips.
The study included more than 4,200 adults ages 20 and older who were part of a nationwide health study. Researchers used a device called a dynamometer to measure each participant's hand strength, adjusting the readings based on body mass index. They found that higher handgrip strength was associated with lower blood pressure, lower triglycerides (a type of fat in the blood), lower blood sugar, and higher HDL (good) cholesterol.
Blood pressure: How low should you go?
A new study suggests greater health benefits with a lower-than-standard number.
Blood pressure has long been one of the best markers of your health. It is a number you can remember and monitor. High blood pressure (hypertension) is linked to a greater risk of heart attacks and strokes.
About one out of three adults has high blood pressure, which is usually defined as a reading of 140/90 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) or higher.
What is masked hypertension?
Image: Thinkstock
Ask the doctor
Q. I know that sometimes people have high blood pressure only at the doctor's office but normal blood pressure at home. But can the opposite also happen?
A. Yes. This phenomenon—when your blood pressure reading is normal at the doctor's office but high at home—is known as masked hypertension. It's hard to know just how common it is, since doctors don't routinely tell people to measure their blood pressure at home if it's normal in the doctor's office or clinic. The only reason we know it exists is from clinical studies that required people to undergo ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. For this type of monitoring, you wear a portable blood pressure cuff and monitor for 24 hours. The machine records your blood pressure every 20 minutes while you're awake and hourly while you're asleep. In these studies, anywhere from 10% to 40% of the participants were found to have masked hypertension, depending on the exact population evaluated.
Your stroke prevention action plan
Image: Bigstock
You get the most bang for your buck from keeping blood pressure in the normal range, but don't skip the other things.
Many tasks are required to run a household. There are groceries to shop for, broken things to fix, and windows to wash. But you need to prioritize: it makes no sense to worry about the weeds in the garden if the mortgage payment is overdue.
Once-a-day blood pressure medication
Ask the doctor
Q. I take my blood pressure medication twice a day. Or at least I am supposed to, but I sometimes forget the second dose because my evenings tend to be really busy. What can I do?
A. One idea is to leave a sticky note on your bathroom mirror or near your bed as a reminder. Or try using an alarm (either a traditional alarm clock or one on a smartphone) that rings close to the time when you normally go to bed. You might also consider taking the second dose with dinner, assuming your doctor or pharmacist says it is okay to take your particular medicine with food.
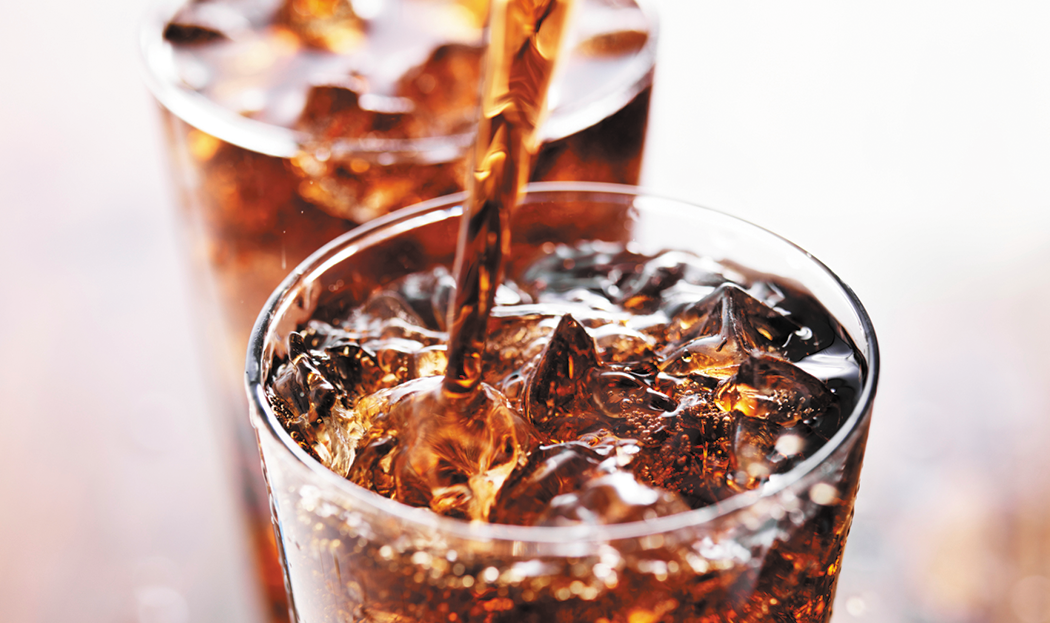
Sugary drinks seem to raise blood pressure
Image: Thinkstock
Research we're watching
Drinking as little as one sugar-sweetened beverage a day is linked to a slightly greater risk of high blood pressure, a new analysis suggests.
Researchers pooled findings from six studies that included a total of more than 240,000 people. They found a 12% higher risk of high blood pressure among people who drank one or more sugary drinks daily compared with those who drank none. Serving sizes of the beverages varied from 7 to 12 ounces among the different studies.
Should you rethink high blood pressure treatment?
Image: Thinkstock
News briefs
Initial results of a large national clinical trial suggest that being more aggressive in treating high blood pressure may save lives. Results of the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) aren't yet published, so we don't know all of the details. But from information released by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in September, it appears that aiming for a systolic (top) blood pressure reading of less than 120 mm Hg may reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure by almost a third, and reduce the overall death rate by 25%. Researchers came to this conclusion after following more than 9,000 middle-aged and older adults with high blood pressure for several years. Half of the participants took an average of two medications and set a target systolic blood pressure of less than 140 mm Hg, the current recommended number. The other half took an average of three medications and aimed for a systolic blood pressure of less than 120 mm Hg. The results in the lower-target group were so impressive that NIH stopped the study early to share the news. Does this mean you should add more pills to your blood pressure treatment? "Not necessarily, because there may be more drug side effects. But if you're aiming for a lower number, I think it will be critical to rely on lifestyle modification, such as stress reduction, diet, salt restriction, and exercise, in addition to medication to lower blood pressure," says Dr. Randall Zusman, a cardiologist and Harvard Medical School associate professor.

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up