5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Controlling Your Blood Pressure Archive
Articles
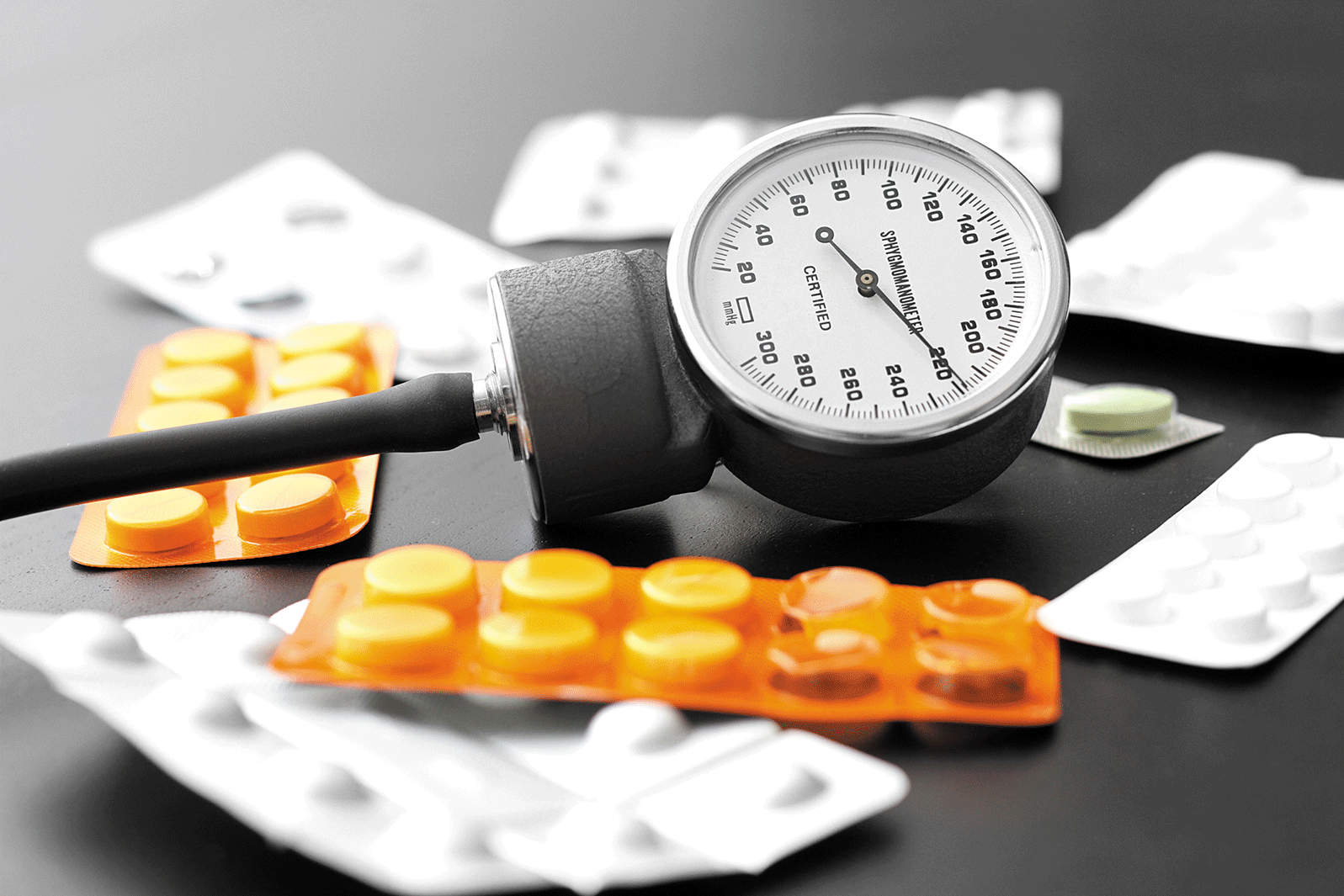
Optimal blood pressure: A moving target?
Image: iStock
If you're concerned about heart disease, discuss your blood pressure target with your doctor.
Earlier this fall, federal officials stopped a major blood pressure study a full year earlier than planned, based on what they called "potentially lifesaving benefits" from the findings. The preliminary results suggest that in people with high blood pressure, achieving a systolic blood pressure (the first number in a reading) of 120 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) in-stead of 140 mm Hg can substantially lower a person's risk of heart attack, stroke, heart failure, and death.
Too much or too little sleep linked to stiffer arteries
Image: Thinkstock
Research we're watching
People who sleep too much or too little may be more likely to have early signs of heart disease, according to a study of more than 47,000 apparently healthy young and middle-aged adults.
The study volunteers filled out sleep questionnaires and underwent tests to assess the arteries in their hearts and legs. Researchers found that people who slept for nine or more hours per night had more calcium buildup in their heart artery walls and stiffer leg arteries than those who slept seven hours per night. These early signs of heart disease were also more prevalent in people who logged five or fewer hours of sleep per night and in people who reported poor sleep quality.
How low should your blood pressure be?
Image: Bigstock
A landmark study indicates that lowering the top number to 120 mm Hg can reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems and death.
Medical practice usually evolves fairly slowly. Experts meet every five to 10 years to review study findings and make recommendations. But occasionally the results of a single study are so decisive that it is brought to a halt early, the results are announced, and doctors change their advice to patients based on the findings. For example, in 2002 the Women's Health Initiative was stopped three years early when postmenopausal women taking estrogen and progestin were found to be at higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and breast cancer than those who weren't on the hormones. The use of postmenopausal hormone therapy fell 70% in the next few years.
When blood pressure dips too low
To avoid feeling dizzy or faint when you first get up in the morning, pump your legs a few times to get your blood flowing before standing up. |
Do you ever feel dizzy or faint when you stand up? Here's one common reason—and what to do about it.
Which blood pressure drug is right for you?
Controlling high blood pressure involves trial and error. It may take more than one medication to do the job, and the dosages may need to be adjusted over time. |
The medications your doctor prescribes may depend on your underlying health issues.
Lifestyle changes for healthy blood pressure
Changing lifelong habits is hard, but these practical tips can help.
When blood pressure persists above healthy limits, men are faced with a decision: take a medication now, or try to lower it with nutrition, exercise, and other lifestyle changes. Many men are reluctant to start taking a new pill every day—possibly for life. Although changing deeply ingrained habits can be hard, it really works.
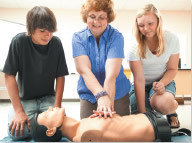
Bystander CPR may help cardiac arrest survivors return to work
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) not only saves lives, it may also help survivors of cardiac arrest recover well enough to return to work, according to a study in the May 12, 2015, issue of Circulation.
Researchers studied more than 4,300 people in Denmark who were employed before they suffered a cardiac arrest. In cardiac arrest, the heart suddenly stops working. More than 75% of survivors who had a cardiac arrest outside a hospital were able to return to work in a median time of four months. Those who received CPR from a bystander were nearly 40% more likely go back to work compared with those who didn't get CPR. The chest compressions given during CPR keep blood circulating to the brain, minimizing brain damage caused by a lack of oxygen.
Stroke risk when you have atrial fibrillation
Now we have a better tool to calculate your chance of a brain attack if you've been diagnosed with afib.
Atrial fibrillation (afib) is among the most common heart rhythm irregularities. During a bout of afib, the usually rhythmic contractions of the heart muscle's upper chambers (the atria) are replaced by an ineffectual quiver that does not completely move blood out of the heart chamber. As a result, blood can stagnate and form clots. These clots can then travel to the brain and cause an ischemic stroke.
When the blood supply to the kidneys suffers
The renal arteries, which supply blood to the kidneys, can become narrowed or blocked—a condition known as renal artery stenosis. Image: Thinkstock |
Fatty plaque in the arteries that feed the kidneys poses a danger to the heart and brain.
Do blood pressure drugs raise your risk of a fall?
Some research has suggested that older people who take blood pressure medications may be prone to falls, perhaps because the drugs make them dizzy or lightheaded when they stand up. But a new study in the May 2015 Hypertension found no increased risk of falls in people taking blood pressure drugs.
For the study, nearly 600 people with chronic high blood pressure reported their falls to researchers via mail-in postcards and phone calls. Almost half of the participants, whose average age was 78, reported one or more falls during the yearlong study. Neither standard nor high doses of blood pressure drugs were linked to falls. In fact, people who took two commonly prescribed types of blood pressure medications—ACE inhibitors and calcium-channel blockers—had a lower rate of falling compared with people not taking those drugs. Given the known benefits of treating high blood pressure in older people, the authors say, withholding blood pressure medication for fear of causing a fall may not make sense.

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up