Recent Articles

Forearm workouts: Strengthening grip for everyday function

Depression symptoms: Recognizing common and lesser-known symptoms

Medication side effects: What are your options?

Independent living with home care assistance: Balancing autonomy and support

Dialysis: What to expect from this life-changing — and lifesaving — treatment

The BEEP program: Keep your balance

Hoarding: What to know about this mental health disorder

21 spices for healthy holiday foods

Listeria: How to protect yourself from this common cause of food poisoning

Adult day care can benefit older adults and their caregivers
Controlling Your Blood Pressure Archive
Articles
Which blood pressure drug is right for you?
Controlling high blood pressure involves trial and error. It may take more than one medication to do the job, and the dosages may need to be adjusted over time. |
The medications your doctor prescribes may depend on your underlying health issues.
Lifestyle changes for healthy blood pressure
Changing lifelong habits is hard, but these practical tips can help.
When blood pressure persists above healthy limits, men are faced with a decision: take a medication now, or try to lower it with nutrition, exercise, and other lifestyle changes. Many men are reluctant to start taking a new pill every day—possibly for life. Although changing deeply ingrained habits can be hard, it really works.
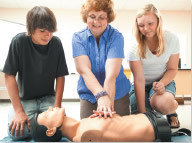
Bystander CPR may help cardiac arrest survivors return to work
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) not only saves lives, it may also help survivors of cardiac arrest recover well enough to return to work, according to a study in the May 12, 2015, issue of Circulation.
Researchers studied more than 4,300 people in Denmark who were employed before they suffered a cardiac arrest. In cardiac arrest, the heart suddenly stops working. More than 75% of survivors who had a cardiac arrest outside a hospital were able to return to work in a median time of four months. Those who received CPR from a bystander were nearly 40% more likely go back to work compared with those who didn't get CPR. The chest compressions given during CPR keep blood circulating to the brain, minimizing brain damage caused by a lack of oxygen.
Stroke risk when you have atrial fibrillation
Now we have a better tool to calculate your chance of a brain attack if you've been diagnosed with afib.
Atrial fibrillation (afib) is among the most common heart rhythm irregularities. During a bout of afib, the usually rhythmic contractions of the heart muscle's upper chambers (the atria) are replaced by an ineffectual quiver that does not completely move blood out of the heart chamber. As a result, blood can stagnate and form clots. These clots can then travel to the brain and cause an ischemic stroke.
When the blood supply to the kidneys suffers
The renal arteries, which supply blood to the kidneys, can become narrowed or blocked—a condition known as renal artery stenosis. Image: Thinkstock |
Fatty plaque in the arteries that feed the kidneys poses a danger to the heart and brain.
Do blood pressure drugs raise your risk of a fall?
Some research has suggested that older people who take blood pressure medications may be prone to falls, perhaps because the drugs make them dizzy or lightheaded when they stand up. But a new study in the May 2015 Hypertension found no increased risk of falls in people taking blood pressure drugs.
For the study, nearly 600 people with chronic high blood pressure reported their falls to researchers via mail-in postcards and phone calls. Almost half of the participants, whose average age was 78, reported one or more falls during the yearlong study. Neither standard nor high doses of blood pressure drugs were linked to falls. In fact, people who took two commonly prescribed types of blood pressure medications—ACE inhibitors and calcium-channel blockers—had a lower rate of falling compared with people not taking those drugs. Given the known benefits of treating high blood pressure in older people, the authors say, withholding blood pressure medication for fear of causing a fall may not make sense.
Getting to the heart of kidney disease
Controlling blood pressure and blood sugar will help both your heart and your kidneys.
On the surface, it's difficult to see how coronary artery disease and kidney damage might be related. But on the cellular level, the two conditions often go hand in hand. A closer look reveals the key. Underlying both conditions are two powerful risk factors: high blood pressure and diabetes, each of which damages the heart and kidneys independently.
Adding folate to blood pressure medication reduces stroke
People with high blood pressure could benefit from a B vitamin known as folate if they are not getting enough from their diets, according to a study in The Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
The study included more than 20,000 adults in China with high blood pressure who had never had a stroke or heart attack. Participants who took folate supplements along with a blood pressure medication had fewer strokes over the four-and-one-half-year trial than those who only took the medication.
Should you worry if you have a fainting spell?
Drinking lots of liquids helps prevent fainting and is especially important in warm weather. Image: Thinkstock |
A fainting spell can be inconsequential, or it can signal a serious health issue. It's important to learn why you faint.
Recent Articles

Forearm workouts: Strengthening grip for everyday function

Depression symptoms: Recognizing common and lesser-known symptoms

Medication side effects: What are your options?

Independent living with home care assistance: Balancing autonomy and support

Dialysis: What to expect from this life-changing — and lifesaving — treatment

The BEEP program: Keep your balance

Hoarding: What to know about this mental health disorder

21 spices for healthy holiday foods

Listeria: How to protect yourself from this common cause of food poisoning

Adult day care can benefit older adults and their caregivers
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up