Recent Articles

Medication side effects: What are your options?

Independent living with home care assistance: Balancing autonomy and support

Dialysis: What to expect from this life-changing — and lifesaving — treatment

The BEEP program: Keep your balance

Hoarding: What to know about this mental health disorder

21 spices for healthy holiday foods

Listeria: How to protect yourself from this common cause of food poisoning

Adult day care can benefit older adults and their caregivers

Digestive enzymes: How supplements like Lactaid and Beano can help with digestion

Can probiotics help calm inflammatory bowel disease?
Controlling Your Blood Pressure Archive
Articles
New thinking about beta blockers
Beta blockers are no longer the first line of defense used to lower blood pressure. |
If you have high blood pressure, there may be better alternatives.
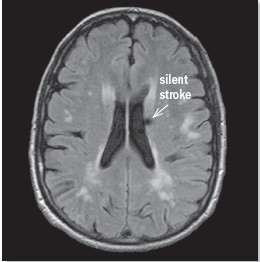
Reduce your risk of silent strokes
As seen on this MRI scan, a silent stroke |
Exercise, eat a healthy diet, and manage blood pressure and cholesterol to lower your odds.
Poor sleep linked to dementia and ministrokes
Images: Thinkstock |
Poor sleep is linked to high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and heart disease. Now a study published in Neurology Dec. 10, 2014, suggests that people with conditions that rob them of oxygen and deep sleep are more likely to have changes in the brain that may lead to dementia. Researchers say conditions such as emphysema and sleep apnea reduce the amount of oxygen in the blood during sleep, which can lead to silent, undetectable "ministrokes." Researchers also found that people who spend less time in deep sleep, called slow-wave sleep, are more likely to have loss of brain cells than people who spend more time in slow-wave sleep. Slow-wave sleep is important in processing new memories and remembering facts. The researchers noted that past evidence has shown that using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine for obstructive sleep apnea may improve cognition, even after dementia has developed. "Sleep quantity and quality are important to maintain optimal health and prevent disease," says sleep expert Dr. Lawrence Epstein, an instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School. "By getting enough sleep, you ensure that you are getting all the types of sleep, which is necessary to maintain proper functioning."
Can memory woes foretell a stroke?
Well-educated people who report memory problems may face a higher risk of stroke.
Minor memory slips—such as losing your keys or forgetting an acquaintance's name—are common as we age. However, people who express concern about their memory may have a heightened risk of stroke, particularly if they're highly educated, according to a study in the January 2015 Stroke.
Can deep, slow breathing lower blood pressure?
Long, slow breaths may help dampen nerve activity that governs your blood pressure. Image: Thinkstock |
A device called RESPeRATE may help, but questions remain.
A new way to "beet" high blood pressure?
Images: Thinkstock |
Beets rarely rank high on anyone's list of most-loved vegetables. But here's a reason to give these ruby-red roots another try: beet juice may help lower blood pressure, according to a study in the February 2015 Hypertension.
Beets contain naturally high levels of nitrates, which your digestive system converts into nitric oxide. This compound relaxes and widens blood vessels, which, in turn, lowers blood pressure.
Chemical in food can liners may boost blood pressure
Images: Thinkstock |
Some plastic bottles, food containers, and linings of cans contain bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical that's been under close scrutiny because of its potential effects on human health. Most Americans have traces of BPA in their urine, and some research hints of a possible link between BPA exposure and cardiovascular disease. Now, a study in the September 2014 Hypertension finds that BPA exposure from cans may raise blood pressure.
Sixty older adults drank two servings of soymilk provided one of three ways: in two glass bottles (providing the least BPA), two cans (most BPA), or one glass bottle and one can. Two hours after participants drank from the cans, their urinary BPA levels were much higher than after they drank from two glass bottles. And their systolic blood pressure (the first number in a blood pressure reading) was roughly 4.5 mm Hg higher after two cans versus two glass bottles.
Treating mild high blood pressure reduces heart problems
A recent study in Annals of Internal Medicine suggests that people with mild high blood pressure and no symptoms of heart disease can still benefit from taking blood pressure medication.
When your blood pressure tips above 140/90 mm Hg, most doctors suggest medication—in addition to healthy diet and exercise. The higher your blood pressure, the greater the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and death. What experts disagree on is how low you should shoot for once your blood pressure is clearly above the 140/90 threshold.
Ask the doctor: Does a beta blocker interfere with exercise?
Q. My doctor recently put me on Tenormin because my blood pressure was getting high. Now, when I run or row, I can't get my heart rate much above 115 beats per minute even though my peak heart rate should be 136. Is the beta blocker keeping me from getting the full benefit of exercise?
A. Although your heart now beats more slowly when you run and row, rest assured that your heart, arteries, lungs, muscles, and the rest of you are getting the full benefit of exercise.
Minerals to manage blood pressure
Are you getting enough calcium, potassium, and magnesium to keep your blood pressure in a healthy range?
Cutting back on salt is the first commandment in controlling high blood pressure, or hypertension. But managing your intake of other dietary minerals also appears to be key. "We're moving beyond just looking at sodium," says Kathy McManus, director of the Department of Nutrition at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. Research from the landmark DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) trial and more recently the OmniHeart study has shed light on the synergy of different foods and the role of minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium in controlling blood pressure.
Recent Articles

Medication side effects: What are your options?

Independent living with home care assistance: Balancing autonomy and support

Dialysis: What to expect from this life-changing — and lifesaving — treatment

The BEEP program: Keep your balance

Hoarding: What to know about this mental health disorder

21 spices for healthy holiday foods

Listeria: How to protect yourself from this common cause of food poisoning

Adult day care can benefit older adults and their caregivers

Digestive enzymes: How supplements like Lactaid and Beano can help with digestion

Can probiotics help calm inflammatory bowel disease?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up