Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Trying to lose weight? Be careful not to lose muscle

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Diseases & Conditions Archive
Articles
Shingles linked with higher risk for heart disease and stroke
People who have had shingles have a 30% increased risk for heart disease and stroke, says a new Harvard study. Learn more about the risk.
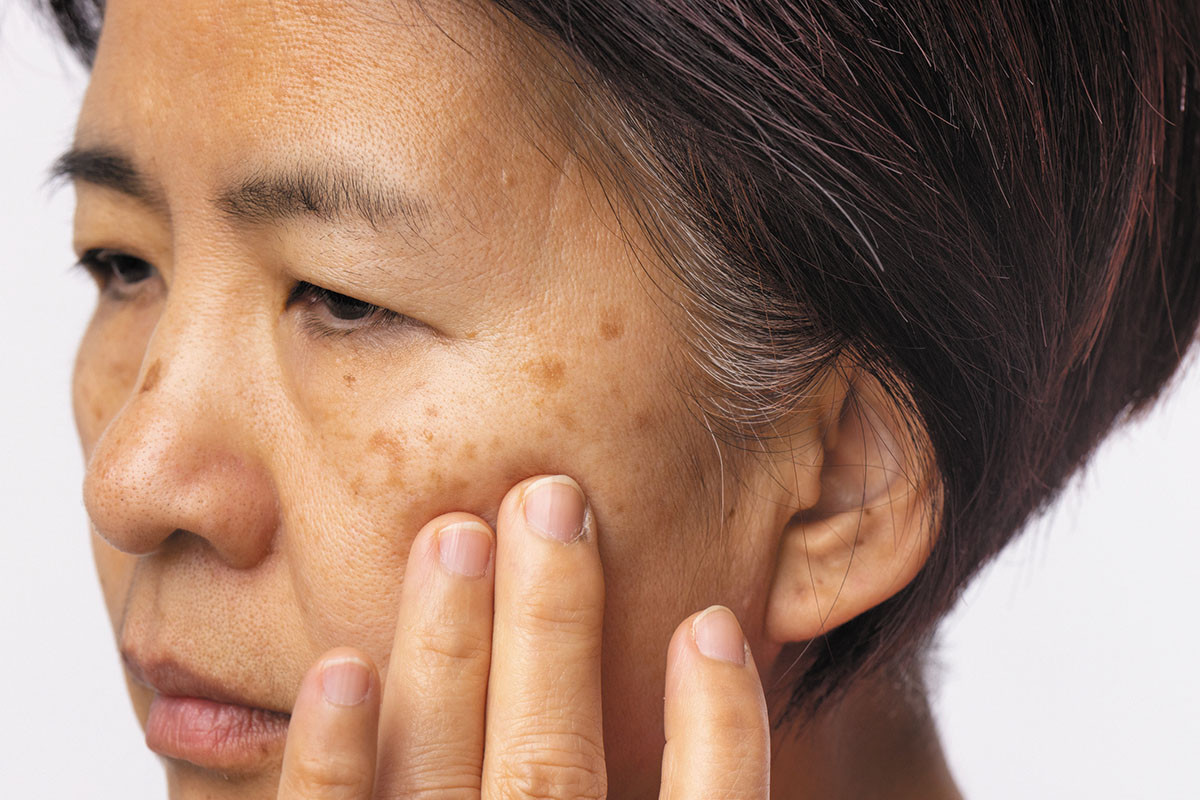
A mask that's hard to shed
Melasma, which causes dark patches on the face, is far more prevalent in women than in men. Dubbed the "mask of pregnancy," melasma triggers include not only pregnancy but also hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and sun exposure. People with darker skin are more prone to it. Melasma is typically treated with topical products that lighten the skin or slough off cells. Laser treatments and chemical peels, however, may worsen melasma. Sunscreen use can help prevent flares.
Vaccination may protect against long COVID
Getting at least one dose of a COVID vaccine lowers the risk of developing long COVID even among people who were previously unvaccinated and recovered from COVID.
The skinny on fatty liver
The body's second largest organ, the liver is responsible for more than 500 bodily functions. One of the liver's greatest threats is nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), an umbrella term that includes several forms of liver disease. Most people with NAFLD have a type known as simple fatty liver. However, up to 20% of people with NAFLD develop inflammation in the liver known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Left unchecked, this more dangerous form can progress into fibrosis (scarring) and potentially cirrhosis (severe scarring and liver damage). Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, increasing exercise, and adopting a plant-based diet are the best means to manage and prevent NAFLD.
Harvard study: Shingles linked to a spike in risks for heart attack and stroke
A 2022 observational study that included more than 200,000 people found that those who'd had shingles at some point had a 30% higher long-term risk for a major cardiovascular event, compared with people who didn't have shingles.
Spot the warning signs of 4 dangerous conditions
Sometimes people miss the symptoms of life-threatening conditions such as a heart attack, a stroke, atrial fibrillation, or a pulmonary embolism. To detect the warning signs, people should pay attention to sudden, new symptoms, especially if they include shortness of breath, chest pain, heart palpitations, lightheadedness, confusion, weakness, fatigue, fainting, or a terrible headache. Someone experiencing any of these symptoms should call 911. If symptoms aren't sudden or intense, and people aren't sure if they warrant emergency help, they should call their doctor.
Over-the-counter hearing aids: What we know so far
Over-the-counter hearing aids are now available in stores and online. They're regulated by the FDA, they don't require a prescription from a doctor, and they're cheaper than prescription hearing aids. But over-the-counter devices are not right for everyone. They're meant only for adults with perceived mild to moderate hearing loss. Before buying a pair, a person should do some homework to find devices with the right fit and features, including a trial period that allows the buyer to return them if they aren't working out.
Seeing a surgeon?
A pre-surgery consultation with the surgeon can feel overwhelming. Many people are anxious and have questions about what's to come. Setting the right expectations on both sides can ease anxiety and help define a successful outcome.
What happens when a drug goes viral?
| After celebrities touted its weight loss benefits, high demand put the diabetes medication Ozempic in short supply. Learn more about what this means for people with diabetes. |
A mindful way to help manage type 2 diabetes?
Lifestyle changes like regular exercise, a healthy diet, and sufficient sleep are cornerstones of self-care for people with type 2 diabetes. But can mind-body practices help people manage or even treat type 2 diabetes? An analysis of multiple studies suggests they might.

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Trying to lose weight? Be careful not to lose muscle

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up