Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine
Diseases & Conditions Archive
Articles
Can shingles raise your risk for heart attack and stroke?
Research we're watching
A research letter published in the July 3 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology says that shingles, a painful rash caused by the varicella-zoster virus (the same virus that causes chickenpox) may be linked to an increased risk of stroke and heart attack.
South Korean researchers used a national medical database to identify diagnoses of shingles, stroke, and heart attack and followed them from 2003 to 2013. They compared 23,213 individuals who had developed shingles during this period and compared their subsequent rates of heart attack and stroke to approximately 23,213 shingles-free individuals. They found that people who had shingles had a 35% higher risk of heart attack and a 59% higher risk of stroke.
Shingles may raise heart attack risk
Research we're watching
Image: © designer491/Thinkstock
People who develop the painful, blistering rash known as shingles may be more susceptible to a heart attack, according to a study in the July 11, 2017, Journal of the American College of Cardiology. Also known as herpes zoster, shingles results from a reactivation of the virus that causes chickenpox, which most adults had during childhood.
Researchers relied on a Korean health database to identify people newly diagnosed with shingles, stroke, or heart attack over 10 years. Among the nearly 520,000 people they followed for that period, just over 23,000 were diagnosed with shingles, whom they compared with a similar number of people without shingles. People who'd had shingles had a 59% higher risk of later having a heart attack and a 35% higher risk of having a stroke compared with people who did not have shingles. The risk was highest during the first year after the onset of shingles and then diminished over time.
What should you do about those unpleasant eye floaters?
Debris in your vision is a nuisance, but you may have to live with it.
Image: © Thinkstock/Thinkstock
Strings, blobs, and cobwebs: they all describe types of specks that may appear to float across your field of vision. These "floaters" are usually just a nuisance. "In many cases, floaters become less noticeable or more tolerable over time, and can even disappear entirely," says Dr. Jeffrey Heier, an ophthalmologist and Harvard Medical School instructor.
But for some people, floaters are distracting to the point of interfering with vision.
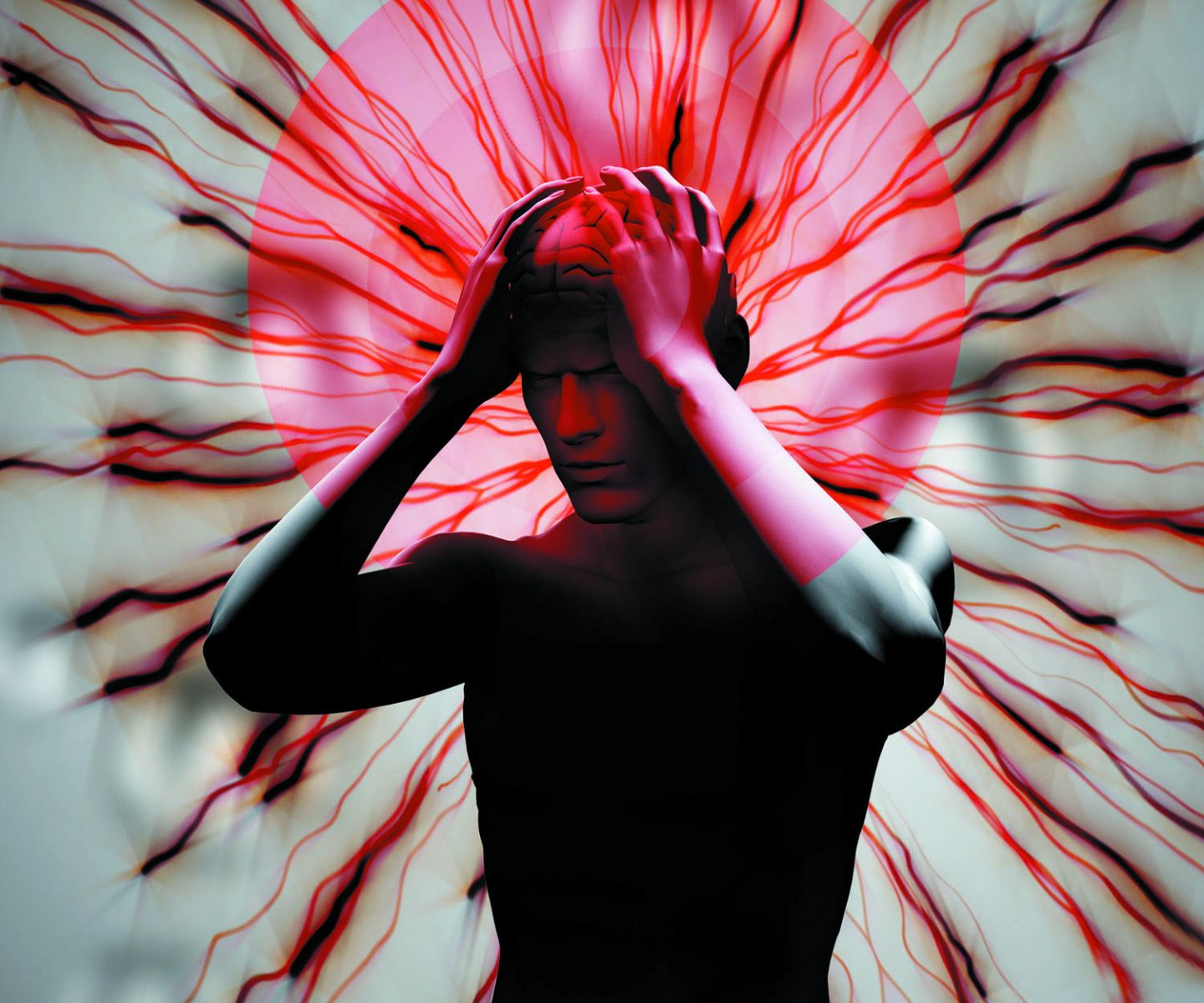
Quick-start guide to headaches
Pain from migraines, cluster headaches, and other types of headaches require very different treatments.
Image: © Wavebreakmedia Ltd/Thinkstock
Pain around the eye and throbbing on one side of the head — they're common headache symptoms, but what do they mean? "Many times people assume a headache is due to sinusitis, and they put up with it for years," says Dr. John Pettinato, a neurologist with Harvard-affiliated Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Understanding your pain can help you find the best approach to treatment.
Should you take an antiviral drug when you get the flu?
One antiviral medication has drawn criticism, but it's still a treatment option.
Image: © kowalska-art/Thinkstock
Bad case of the flu? Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza), may reduce symptoms and help you recover from the flu a day or two earlier. But oseltamivir came under fire a few months ago for a lack of effectiveness.
In June, the World Health Organization (WHO) removed oseltamivir from its list of essential medicines. "Their decision was based on the relatively low effectiveness of oseltamivir in clinical trials and clinical practice. I suspect this is due to a significant number of people who started therapy after their flu symptoms had been going on for more than two days," says Dr. Paul Sax, an infectious disease specialist and Harvard Medical School professor.
Have you checked your blood sugar lately?
News briefs
Many Americans may be living with the precursor condition to type 2 diabetes without even knowing it, according to a report released July 18, 2017, by the CDC. The National Diabetes Statistics Report found that more than 84 million people in the United States likely have prediabetes — higher-than-normal blood sugar levels.
Prediabetes can turn into full-blown type 2 diabetes — meaning the body doesn't respond to insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb blood sugar for energy. Type 2 diabetes increases the risk for vision loss; heart disease; stroke; kidney failure; amputation of toes, feet, or legs; and even early death. The report found that almost one in four people with diabetes is undiagnosed.
Is my ear problem related to my age?
Ask the doctors
Image: © Catherine Yeulet/Thinkstock
Q. A friend and I both recently had ear blockages caused by impacted earwax. Is this something that becomes more common with age, or is it just a coincidence?
A. It's not just a coincidence. Earwax blockages definitely increase with age. While blockages affect only 5% of healthy adults, they occur more often in older people, with 57% of nursing home residents experiencing this problem, according to the American Academy of Family Physicians.
A silent heart threat may actually be endangering your brain
Want to keep your mind sharp? Be aggressive about treating your high blood pressure.
Image: © adrian825/Thinkstock
If you're like a lot of people, you probably think of your heart when you think about blood pressure. But you should also think about your mind.
"High blood pressure is not just a disease or condition. It's actually a risk factor. It's a risk factor for heart disease and stroke, and it's a risk factor for cognitive decline and dementia," says Dr. Natalia Rost, a stroke neurologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and associate professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School.
Frequently asked questions about colds and the flu
Here are the answers to six commonly asked questions about colds and the flu.
Q. When should I stay home from work or keep my child home from school?
Avoiding health risks at the farmers’ market
Watch out for unpasteurized products, and ask vendors about food safety.
There's something magical about strolling through a farmers' market on a crisp autumn morning. The fruit and vegetables seem fresher there than they do in a store — apples taste tarter, tomatoes seem redder and riper. It's a farm-to-table connection that puts you in touch with nature and the harvest.
Maybe that's partly behind the explosion of farmers' markets across the country, climbing from about 2,000 markets in 1994 to more than 8,600 today, according to the Farmers Market Coalition. "It's a great way to get fresh produce and try different foods you may not have come across before. But it should be enjoyed with caution," urges Dr. Simi Padival, an infectious disease specialist with Harvard-affiliated Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up