Counting steps is good — is combining steps and heart rate better?

Appendix pain: Could it be appendicitis?

Can saw palmetto treat an enlarged prostate?

How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond

Zinc: What it does for the body, and the best food sources

Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?
Exercise & Fitness Archive
Articles
Easy ways to fight pandemic-era inactivity
Interrupt your sitting time with a break every hour.
For many people, the effects of the pandemic include less physical activity. But long periods of sitting are bad for health. They're associated with increased risks for obesity, diabetes, heart disease, stroke, cancer, and metabolic syndrome (a cluster of health conditions that include abdominal obesity, unhealthy cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, and high blood sugar). Too much sitting is even linked to an early death. The good news: staying active throughout the day helps reverse the effects of too much sitting.
Doctor's orders
"Take a two-, five-, or 10-minute break at least once per hour," advises Dr. Beth Frates, director of wellness programming for the Stroke Research and Recovery Institute at Harvard-affiliated Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital.
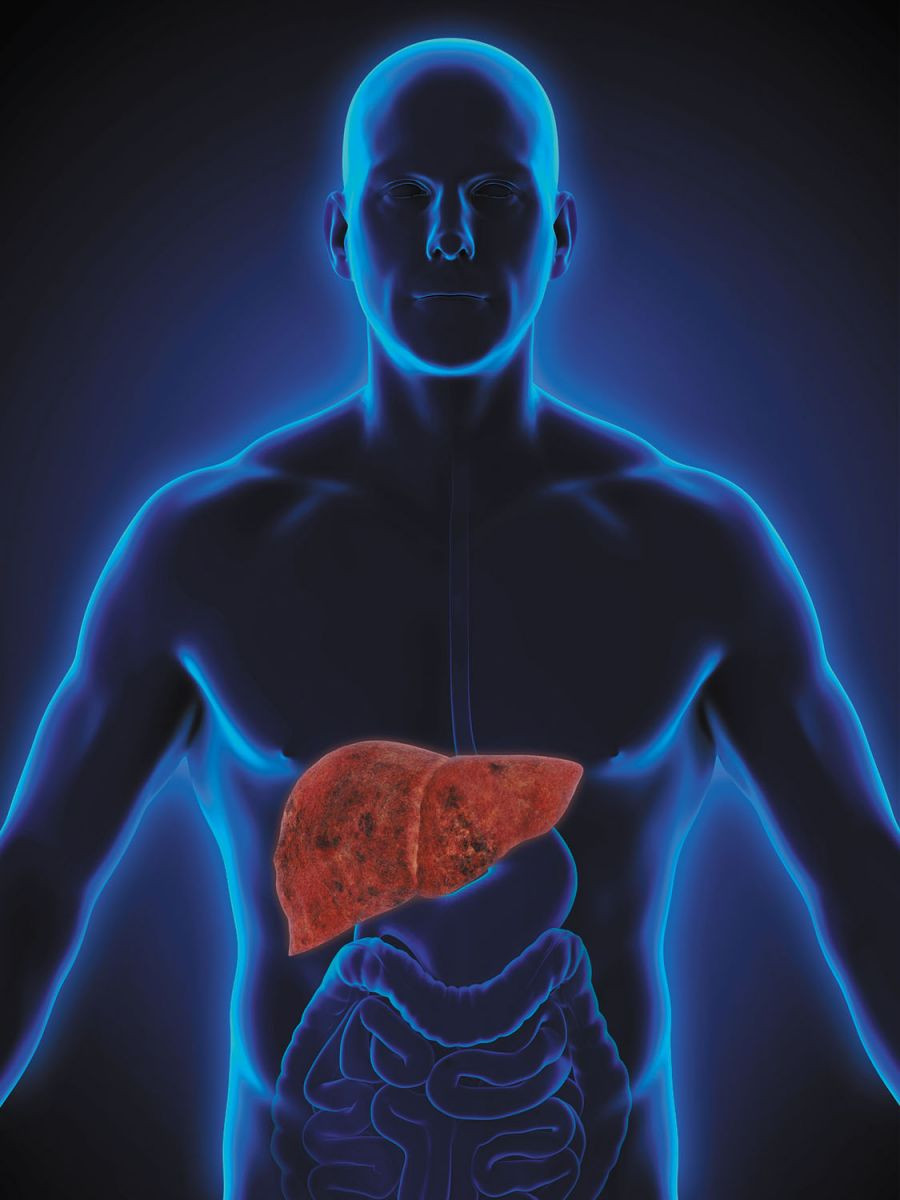
The skinny on fatty liver disease
Rates continue to rise, but there are ways to protect yourself and even reverse the effects of this dangerous disorder.
Your liver is your largest internal organ and your body's workhorse. Among its many jobs are converting food into fuel, processing fat from your blood, clearing harmful toxins, and making proteins that help your blood clot. Yet this hard-working, supersized organ is susceptible to a dangerous and often hard-to-diagnose condition called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD.
NAFLD is defined as the presence of fat in more than 5% of liver cells. It is the most common liver disease and affects up to 25% of American adults, 60% of whom are men.
Recharge your sexual energy
If lack of energy has drained your sex life, there are ways to reignite the passion.
Image: © nautiluz56/Thinkstock
Your sexual drive can stay high late in life, but often your energy for sex can diminish. Low energy not only affects your sex life, but can carry over to other parts of your life, too. You can become apathetic, no longer find pleasure in favorite activities, and become more sedentary.
However, many of these issues related to lost sexual energy can be addressed. "Never think lack of energy means an end to your sex life, and there is nothing you can do about it," says Dr. Sharon Bober, director of the Harvard-affiliated Dana-Farber Sexual Health Program. "There are many strategies you can adopt to get back in the game."
New guidelines for aches, pains, and strains
When a minor injury leads to soreness or discomfort, what’s the best first treatment choice? The American College of Physicians and the American Academy of Family Physicians recently developed new recommendations based on reviews of more than 200 studies involving nearly 33,000 subjects.
Stretching may improve blood vessel health
Research we're watching
Doing easy leg stretches may improve blood flow throughout the body by making the arteries more flexible and able to dilate, according to a small study in the July 1, 2020, Journal of Physiology.
The study included 39 young adults, 27 of whom did passive leg stretches five times a week for 12 weeks, while the other 12 did no stretching. (Passive stretching involves holding a stretch for a set period of time aided by an outside force, such as one's body weight or gravity). Volunteers held the thigh and calf stretches for 45 seconds, followed a 15-second rest. They repeated each set a total of five times.
Protect your bones with tai chi
This ancient practice, which consists of sequences of fluid movements, can improve your balance and help you prevent falls.
Tai chi is a form of gentle exercise that experts say can help improve your mood, reduce your stress level, and help keep your heart healthy. It can also benefit your bones.
"There's very strong evidence that tai chi is one of the best weight-bearing exercises to reduce the risk for falls," says Peter Wayne, faculty editor of the Harvard Special Health Report An Introduction to Tai Chi and director of the Osher Center for Integrative Medicine.
Stop counting calories
Put the focus on food quality and healthy lifestyle practices to attain a healthy weight.
Most people have been taught that losing weight is a matter of simple math. Cut calories — specifically 3,500 calories, and you'll lose a pound. But as it turns out, experts are learning that this decades-old strategy is actually pretty misguided.
"This idea of 'a calorie in and a calorie out' when it comes to weight loss is not only antiquated, it's just wrong," says Dr. Fatima Cody Stanford, an obesity specialist and assistant professor of medicine and pediatrics at Harvard Medical School.
Reinvent your walking regimen
Switch the type of walking in your routine to stay motivated and active.
Putting one foot in front of the other is a simple way to trigger a cascade of health benefits. Regular brisk walks help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol; control blood sugar; and reduce the risk for high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Brisk walks also strengthen muscles, burn calories, and lift mood.
Just one problem: some people find walking boring. Boredom may diminish your motivation and interest in exercising. Before that happens, mix up your regimen with different types of walking that maximize physical, mental, and emotional health benefits.
Leg stretching may improve blood flow and prevent strokes
In the journals
Not only can regular leg stretching help reduce cramps and muscle strains, it also may be another way to protect against heart disease and stroke. A study published online July 1, 2020, by The Journal of Physiology found that performing simple leg stretches can help improve blood flow throughout the body.
Researchers split 39 healthy people into two groups. One group didn't do any stretching. The other group performed four types of leg stretches five times a week for 12 weeks. The stretches focused on the hip, knee, and ankle. Each stretch was done for 45 seconds with a 15-second recovery. Afterward, the researchers found that the arteries in the lower legs of the stretching group had better blood flow and less stiffness. The stretching group also had lower blood pressure at the end of the study compared with their initial readings.

Counting steps is good — is combining steps and heart rate better?

Appendix pain: Could it be appendicitis?

Can saw palmetto treat an enlarged prostate?

How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond

Zinc: What it does for the body, and the best food sources

Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up