Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine

Dragon fruit: How to enjoy this antioxidant-rich fruit
Headache Archive
Articles
FDA approves first migraine prevention drug
News briefs
Encouraging news for people who suffer with migraines: in May, the FDA approved erenumab (Aimovig), the first medication aimed at preventing these debilitating headaches. Current medications to treat migraines were actually designed to control other conditions, such as seizures or an irregular heartbeat; their side effects (like sexual dysfunction and fuzzy thinking) often cause people to skip treatment. Erenumab offers a new approach. Injected once a month, it works by blocking a molecule (calcitonin gene-related peptide) involved in migraine attacks, and compared with other drugs, it appears to have fewer side effects (primarily constipation and injection site reactions). "This drug is for people who have more than four migraines per month, but it won't take migraines away entirely," says Dr. Gad Marshall, a neurologist at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. Clinical trials suggest it can reduce frequency by one or two migraines per month, or even more in some people. "For people with frequent debilitating migraines it could be a game changer," says Dr. Lee Schwamm, a neurologist at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital. "But erenumab is expensive, and it will take time to find out if it's effective and safe over the long term."
New drug shows promise for preventing migraines
In the journals
Image: © Wavebreakmedia/Getty Images
Migraine sufferers may be able to prevent future attacks with a new medication called galcanezumab, suggests a study published online Dec. 18, 2017, by JAMA Neurology. Currently, there are five FDA-approved drugs for migraines, but none were designed specifically for treating attacks or addressing the mechanisms at work.
In comparison, galcanezumab works to suppress the activity of calcitonin gene–related peptide (CGRP) in people. That molecule is believed to play an integral role in migraines and cluster headaches.
New ways to manage migraines
Sufferers now have more options than ever to ease the pain or even ward off attacks.
Image: © YakobchukOlena/Thinkstock
If you've ever experienced a migraine, you know it's no ordinary headache. Not only does it cause throbbing pain, typically on one side of your head, but it may also cause vision changes, sensitivity to light, and nausea. It's the type of headache that makes you want to retreat to a dark, quiet room and stay there until it goes away. Recovering from a migraine can take time; the headache can last for hours or days. Migraines affect an estimated 28 million women in the United States, according to the American Migraine Foundation (AMF).
The World Health Organization says that migraine headaches rank in the top 10 of disabling conditions. These headaches result in lost work days, lost productivity, and high health care costs. And of course, they can cause you to miss out on pleasurable activities and time with family.
Headache basics
Despite the fact that headaches are extremely common, doctors don't fully understand exactly why or even how they occur. Neither the skull nor the brain is sensitive to pain, but both are surrounded by pain-sensitive membranes. Most headache pain stems from abnormalities in these membranes or nearby muscles, blood vessels, or nerves—either alone or in combination.
Women are twice as likely as men to experience moderate and severe headaches and more likely to experience certain types of headaches, such as migraine. A major reason is fluctuating hormone levels that are part of the monthly menstrual cycle.
Quick-start guide to headaches
Pain from migraines, cluster headaches, and other types of headaches require very different treatments.
Image: © Wavebreakmedia Ltd/Thinkstock
Pain around the eye and throbbing on one side of the head — they're common headache symptoms, but what do they mean? "Many times people assume a headache is due to sinusitis, and they put up with it for years," says Dr. John Pettinato, a neurologist with Harvard-affiliated Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Understanding your pain can help you find the best approach to treatment.
What causes ice cream headache?
Q. What exactly happens when I eat something cold and get an ice cream headache? Is it harmful in any way?
A. Ice cream headache, also known as "brain freeze" or cold-stimulus headache, is a headache some people get when they consume a cold food or beverage quickly. The pain is usually in the forehead or both temples, and it usually lasts less than five minutes.
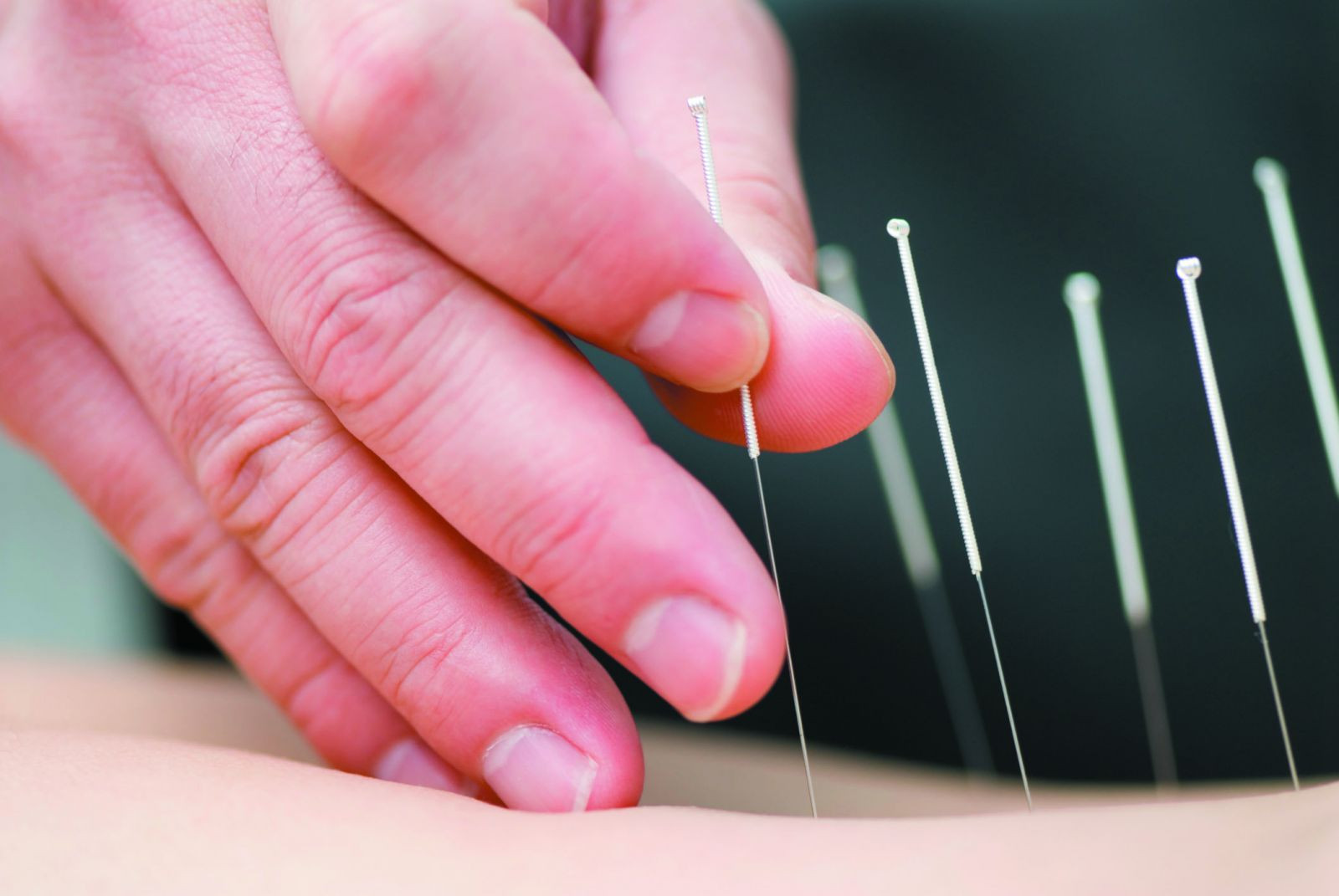
The finer points of acupuncture
This ancient practice can be used alone or with conventional therapy to help ease your pain.
Image: © zilli/Thinkstock
Men looking for an easy and effective means to manage pain should consider acupuncture.
"There are many different types of pain — neuropathic, muscular, degenerative joint — all of which can make management complex," says Hugo Lopez, a licensed acupuncturist with Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center. "Sometimes you need to treat not just the physical components, but also the psychological ones, and that is where acupuncture can help, as it addresses both problems."

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine

Dragon fruit: How to enjoy this antioxidant-rich fruit
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up