New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that’s healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux
Heart Disease Archive
Articles
Understanding exercise heart rate zones
Exercise heart rate zones reflect different percentages of a person's estimated maximum heart rate. While some people find it helpful to monitor their heart rate zone during exercise, consistently engaging in physical activity is the most important priority.
Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve
A narrowed aortic valve (aortic stenosis) affects about one in 20 people over age 65. Medical therapies for treating this progressive disease are under investigation, and a recent study explored the potential benefits of proactive valve replacement.
When and why you need drugs for atrial fibrillation
Many people with atrial fibrillation — a rapid, irregular heart rhythm — need medications to control symptoms and lower their risk of stroke. These include drugs that slow down the heart, help restore its rhythm, and prevent blood clots.
New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain
Carotid artery stenosis, which happens when fatty plaque accumulates in neck arteries that supply the brain, leaves people vulnerable to a stroke. Intensive drug therapy may forestall the need for invasive procedures to treat this problem.
New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart
A 2025 study suggests that polyphenols, found in a wide range of plant foods, may have long-term benefits for the heart. Over an average of 11 years, people whose diets contained the most polyphenol-rich foods ranked lowest on scores of heart disease risk.
Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence
People with atrial fibrillation (afib) who drank an average of one cup of caffeinated coffee daily had a lower risk of recurrent afib compared to those who avoided caffeine, according to a 2025 study.
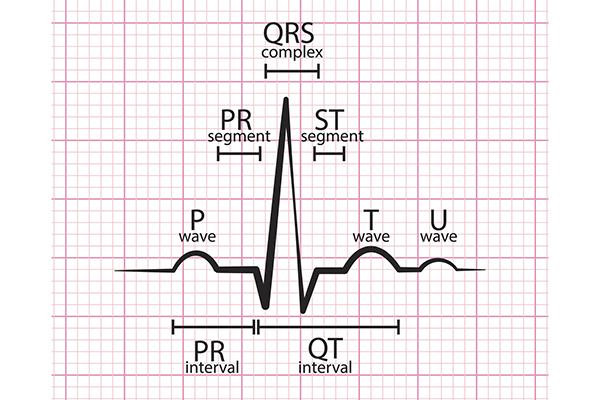
What is long QT syndrome?
Long QT syndrome is a disorder of the heart’s electrical system that can be either acquired (for example, due to a medication) or congenital. Although usually people have no symptoms, it can cause a fast, erratic heartbeat that may lead to shortness of breath, fainting, and sometimes death.
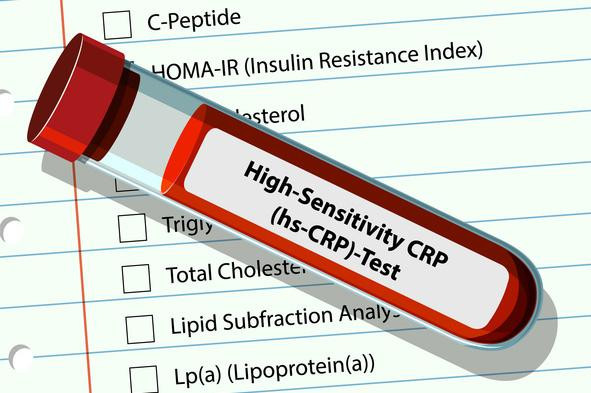
Inflammation and heart disease: A smoldering threat
Chronic, low-level inflammation is just as important as cholesterol in causing clogged heart arteries. Cardiologists are calling for more widespread testing for inflammation, which is easily measured with an inexpensive blood test.
New thinking on beta blocker use
Beta blockers have long been standard treatment for people after a heart attack. New evidence suggests they may not help those whose hearts still pump normally, though the drugs remain important for heart attack survivors with reduced ejection fraction.
What to know about heart palpitations
Heart palpitations are sensations of a pounding or racing heartbeat, often triggered by stress, stimulants, or hormonal changes. They’re usually harmless but should be checked by a doctor. Palpitations may improve with lifestyle changes or treatment for underlying conditions.

New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that’s healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

How to curb your stress eating

How to spot Parkinson’s disease symptoms

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they’re different

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up