New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that's healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

How to spot Parkinson's disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

How to curb your stress eating

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they're different
Heart Health Archive
Articles
Sleep apnea treatment lowers rehospitalization for heart problems in older adults
A 2022 study found that older adults with sleep apnea who are hospitalized for cardiovascular disease are far less likely to be rehospitalized within 30 days if they consistently treat their apnea with CPAP therapy, which keeps the airway open during sleep.
Novel procedure may lower stubbornly high blood pressure
Renal denervation is a minimally invasive procedure that destroys some of the nerves inside the renal arteries, which supply the kidneys. The procedure lowers blood pressure by disrupting communication between the brain and the kidneys that leads to elevated blood pressure. People with stubbornly high blood pressure may be candidates for the procedure, which is currently approved for use in Europe but not in the United States.
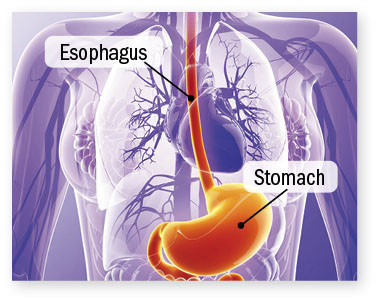
Heart disease and heartburn: What's the overlap?
Heartburn can cause chest pain that may be mistaken for a heart attack, and vice versa. Heartburn causes more a burning sensation and is more likely to occur after a large meal. Heart attacks are often described as a feeling of tightness or pressure and are more likely to occur after physical activity or stress. People who aren't sure about their symptoms should get to an emergency room for an evaluation as soon as possible.
Sugar substitutes: New cardiovascular concerns?
People who use artificial sweeteners such as aspartame (NutraSweet, Equal), acesulfame potassium (Sunnett, Sweet One), and sucralose (Splenda) may have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease compared with people who avoid these products. These zero-calorie sweeteners might not help people lose weight, and experts postulate that artificial sweeteners may trigger inflammation and alter normal metabolism, the gut microbiome, and blood vessels in ways that promote type 2 diabetes, unhealthy cholesterol levels, and high blood pressure.
The many ways exercise helps your heart
Aerobic and muscle-building exercises can trigger physiological changes that improve blood vessels and metabolism in ways that help prevent all the major risk factors that contribute to heart disease. These include high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and unhealthy cholesterol levels. Exercise can also improve mental health problems such as depression and stress, which are common but underrecognized risks for heart disease.
A breath-robbing disease that's hard on the heart
About one in eight adults over age 45 has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). COPD refers to several lung-damaging conditions, particularly emphysema and chronic bronchitis, that cause coughing and breathlessness. But many people don't know much about COPD, which is largely caused by cigarette smoking and may be mistaken for heart disease. Anyone with symptoms of COPD should be evaluated by a physician. People who have heart disease who have ever smoked or lived with a smoker should be tested for COPD.
Shining a light on thoracic aortic disease
A thoracic aortic aneurysm can be small and stable, or it can tear or rupture. People with certain genetic conditions, and those who have a relative who has had this condition, are at higher risk and should be tested.
The inside story on pacemakers
The likelihood of someone needing a pacemaker increases with age. This tiny battery-powered device, implanted into the chest, improves abnormal heart rhythms and improves blood flow if the heart does not pump effectively. By helping the heart maintain more normal function, pacemakers enable many individuals with certain heart conditions to resume their normal lifestyle and stay active longer.
Some heart patients need antibiotics before dental work
People with certain heart conditions, including a replaced or repaired heart valve, should take antibiotics before invasive dental procedures. This helps prevent endocarditis, a serious heart infection often caused by bacteria from the mouth.

New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain

Want to prevent shifting teeth? Maybe you need retainers

What you need to know about the new dietary guidelines

Food that's healthier for people and planet can be cheaper, too

New evidence that polyphenol-rich foods help the heart

How to spot Parkinson's disease symptoms

8 simple ways to reduce ultra-processed foods in your diet

GERD diet: Foods to avoid to reduce acid reflux

How to curb your stress eating

Heart failure symptoms in women: How they're different
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up