Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine
Men's Health Archive
Articles
Emergencies and First Aid - Heimlich Maneuver on an Adult
Heimlich Maneuver on an Adult
| ||||
Emergencies and First Aid - Heimlich Maneuver on a Child
Heimlich Maneuver on a Child
| ||
Emergencies and First Aid - Heimlich Maneuver on an Infant
Heimlich Maneuver on an Infant
| ||||
Do not get sold on drug advertising
Prescription drug ads are a multibillion-dollar industry that promotes treatments you may or may not need. Here's how to use that information to your advantage.
Ads for prescription drugs are everywhere. You can't watch a sporting event without seeing an ad touting a treatment for erectile dysfunction, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or joint pain.
Drug marketing is a big business, and companies are willing to spend a lot of money to offer you an easy solution to a health problem you may or may not have. From 2012 to 2015, yearly spending on prescription drug advertising in all media outlets (except digital) rose from $3.2 billion to $5.2 billion, and that figure is expected to only go up.
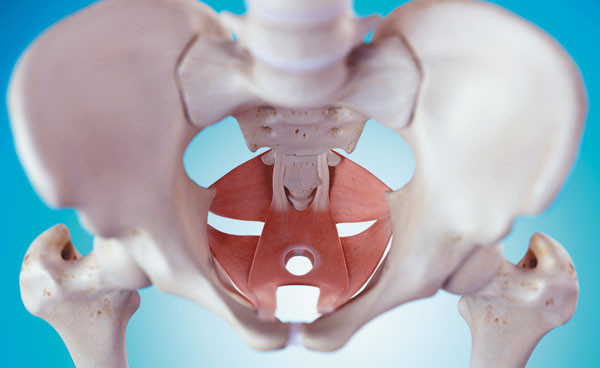
Kegels: Not for women only
Women use kegels to strengthen their pelvic floor muscles, but men may also benefit from doing these exercises.
Image: © Eraxion /Thinkstock
Kegel exercises to strengthen pelvic floor muscles have long been seen as just for women, but they may be a way for men to address some common unpleasant issues as they age.
"Men also can have issues with these muscles, which can cause urinary leakage, bowel trouble, and even erection problems," says physical therapist Celia Brunette, with Harvard-affiliated Spaulding Rehabilitation Center.
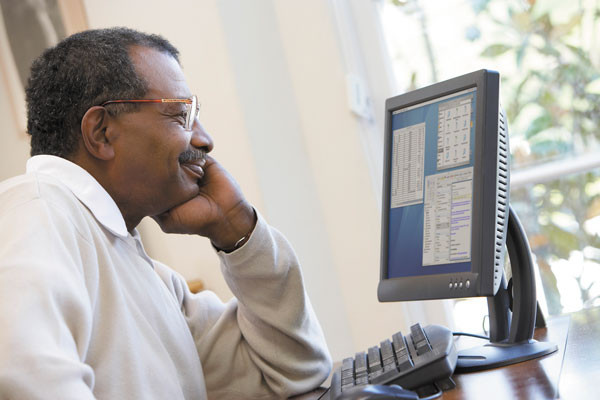
Help with online health
Frustrated by medical and health care websites? New research suggests seniors don't use this health technology like they should, but it may not be their fault.
Image: © BananaStock/Thinkstock
It's said that you can find just about anything on the Internet. Yet when it comes to finding information about health, many seniors are at a loss.
"Few seniors are using digital health technology," says Dr. David Levine, of Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital, who specializes in medical technology information.
Possible link between shoulder problems and heart disease risk
Shoulder pain appears to be associated with risk factors for heart disease. Researchers found that people with the most heart disease risk factors, like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes, were almost five times more likely to also have shoulder trouble.
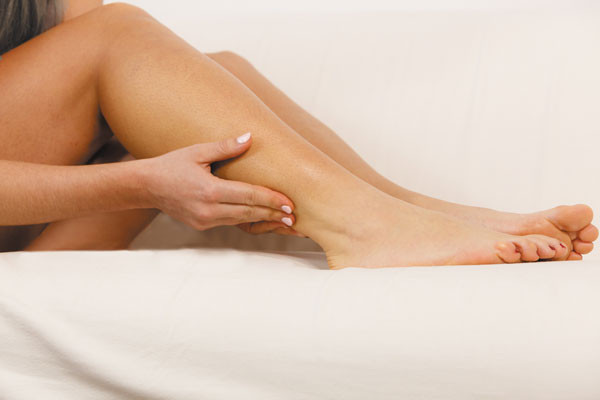
Is there hope for leg cramp sufferers?
Despite the lack of a universally recognized therapy for nighttime leg cramps, a few approaches may be worth trying.
Image: Monkey Business Images/Thinkstock
Few things are more jarring to a night's sleep than shooting calf pains. If you have nocturnal leg cramps, you have lots of company. Although they can strike people at any time of life, they become more common with age. Among people over 60, almost half report having leg cramps, a third say they are awakened by cramps at night, and 15% report weekly episodes.
What causes leg cramps?
Preventing cramps
There are no FDA-approved medications for leg cramps, and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force hasn't issued guidelines for treating them. However, the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) has issued the following advice on common therapies, based on scientific evidence of effectiveness.
Stretching exercises. The AAN says that there are not enough data to say for sure that stretching helps reduce the frequency of muscle cramps. That doesn't mean that the exercises are ineffective or harmful, and doing them can help contribute to the flexibility of your legs.
Quinine. There is solid evidence that quinine and quinine derivatives are effective in reducing the frequency of muscle cramps, although the magnitude of benefit is small. However, quinine is out-of-bounds for most people. The FDA has issued repeated warnings against using quinine (which is approved only to treat certain types of malaria) to prevent or treat leg cramps because it may cause serious side effects, including bleeding and kidney damage. Although doctors can still prescribe quinine, it is recommended only when cramps are disabling and when the person can be carefully monitored for side effects.
Vitamin B complex. There is some evidence that taking a daily capsule containing eight B vitamins—B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6, B7 (biotin), B9 (folate), and B12—may prevent cramps.
Calcium-channel blockers. Evidence indicates that one calcium-channel blocker—diltiazem (Cardizem, Dilacor XR)—is possibly effective.
Ineffective therapies. The AAN found enough evidence to indicate that magnesium supplements and gabapentin (Neurontin) aren't likely to help.
Other remediesIn situations like nighttime leg cramps, where there are no widely accepted treatments, unproven remedies may be worth a try. The following are low-risk and have enthusiastic proponents.
|
Look on the bright side and maybe even live longer
Studies suggest that adopting a sunnier outlook may improve your health and even extend your life.
Image: © lzf /Thinkstock
In these turbulent times, it's sometimes a struggle to maintain a glass-half-full view of life. But if you can, it may serve you well. A growing body of research links optimism—a sense that all will be well—to a lower risk for mental or physical health issues and to better odds of a longer life.
One of the largest such studies was led by researchers Dr. Kaitlin Hagan and Dr. Eric Kim at Harvard's T.H. Chan School of Public Health. Their team analyzed data from 70,000 women in the Nurses' Health Study who, in 2004, had answered questions about how they viewed their futures
White wine linked to higher risk of certain melanomas
Data from more than 200,000 people indicates that the risk of developing melanoma increases by 13% for every glass of white wine consumed per day. Drinking beer, red wine, or liquor was not associated with increased risk.

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up