Recent Articles

An action plan to fight unhealthy inflammation

How to treat spider bites and when you need to see your doctor

Gratitude enhances health, brings happiness — and may even lengthen lives

Skin care for aging skin: Minimizing age spots, wrinkles, and undereye bags

Medicare versus Medicaid: Key differences

Prostate cancer: Short-course radiation as effective as longer-term treatments

Lost a tooth? What to know about dental implants

Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Evidence-based uses and unproven claims

Gatorade. Liquid IV. Do you need extra electrolytes?

Sexual violence can cast a long shadow on health
Mental Health Archive
Articles
To the point: Here’s what parents should know and do about Netflix’s To the Bone
A Netflix original movie about a young woman’s struggle with anorexia nervosa is raising questions among parents about whether the movie might glamorize the disorder, and how best to talk to children about this topic.
Midlife depression probably not a risk factor for dementia
In the journals
A study published online May 17, 2017, by JAMA Psychiatry found that while depression symptoms later in life were associated with dementia, having symptoms in midlife was not. The findings indicate that depression may not be a risk factor for dementia as previously thought, according to the researchers. In the study, about 10,000 people (two-thirds of them men), ages 35 to 55, were recruited and followed for 28 years. Those who reported chronic or recurring depression symptoms at the study's beginning did not show a significant increased risk of developing dementia by the study's end. However, those who reported depression symptoms within the final 11 years of the study were twice as likely to be diagnosed with dementia.
The researchers said that if depression symptoms were a true risk factor for dementia, there would be an association with people who had symptoms earlier in life and not just later. They concluded that depression later in life instead might be an early sign of dementia.
Exercise today, look better tomorrow (really)
A small study supports the idea that exercising improves body image, whether or not the activity leads to any visible change in appearance. This suggests that additional research examining different types of exercise, and the long-term psychological effects of physical activity would be valuable.
4 tricks to rev up your memory
Stay ahead of age-related changes in thinking skills by making the most of your brain's memory process.
We all have moments of forgetfulness about where we put the keys, why we walked into a room, or what an object is called. Most likely, this reflects age-related changes in thinking skills. "In terms of brain function, everyone has a decline over time in all areas, with the exception of vocabulary," says Dr. Joel Salinas, a neurologist specializing in behavioral neurology and neuropsychiatry at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.
How memory works
Memory involves three processes: encoding, recording, and retrieval. The brain receives and encodes (takes in) new information; the brain then records (stores) the information; finally, the brain retrieves information when you need it.
Exercise and better thinking skills: More evidence for a possible link
News briefs
Image: © Horsche/Thinkstock
A review of research published online April 24, 2017, by the British Journal of Sports Medicine suggests that physical exercise may help improve thinking skills in adults ages 50 or older, regardless of their mental performance when they started exercising. Researchers combed through 39 randomized controlled trials that looked at this age group. Most of the studies involved people who did aerobic exercise (the kind that gets your heart and lungs pumping, like brisk walking), resistance training (the kind that works your muscles and bones, like weight lifting), or a combination of aerobics and resistance training. A handful of the studies involved people who did yoga or tai chi. In all of the studies, participants took tests that measured various aspects of thinking skills — such as attention, working memory, and the ability to plan, organize, and manage time. All exercise types but yoga appeared to have benefits for the brain. The authors say the exercise regimen with the biggest brain boost was a combination of both aerobic and resistance-type training, of at least moderate intensity, for at least 45 minutes per session on as many days of the week as possible. The takeaway? Start exercising, and incorporate resistance training into your weekly routine.
Can drinking tea prevent dementia?
In the journals
Image: © jimfeng/Thinkstock
A study in the December 2016 Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging showed that drinking tea frequently is associated with a lower risk of dementia, especially for people who are genetically predisposed to the disease.
Researchers followed 957 older adults, average age 65, who were part of the Singapore Longitudinal Aging Study. Of these, 69% drank tea on a frequent basis. After a five-year period, the researchers found that the tea drinkers had a 50% lower risk of dementia. This is consistent with earlier findings that showed tea consumers scored higher on various cognitive tests.
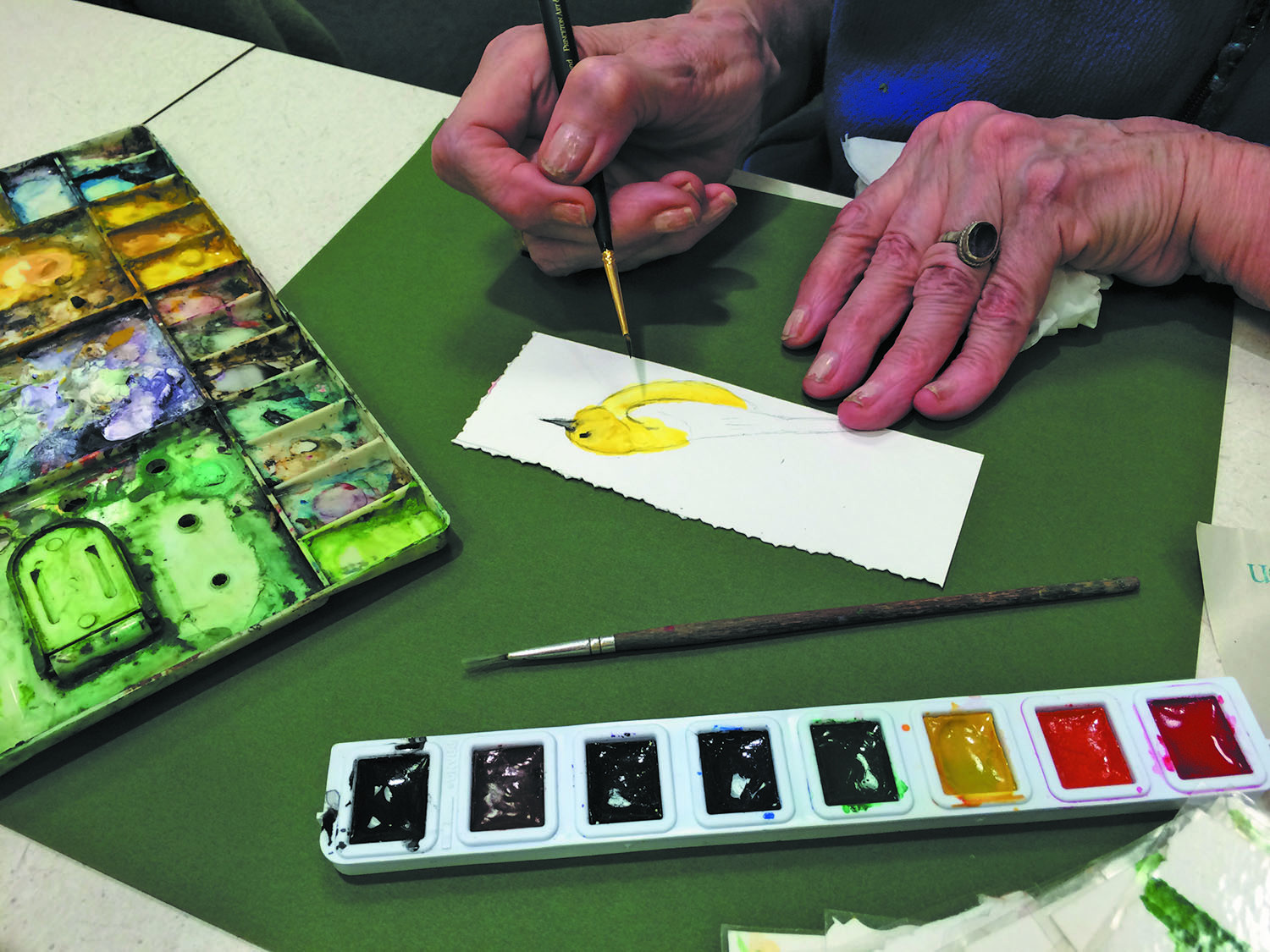
The healing power of art
Creative activities can relieve stress, aid communication, and help arrest cognitive decline.
Image: © Katherine A. Gallagher Integrative Therapies Art Therapy Program at the Mass. General Cancer Center
The title of a recent documentary film, I Remember Better When I Paint, sums up the findings of a growing body of research into the cognitive effects of making art. The movie demonstrates how drawing and painting stimulated memories in people with dementia and enabled them to reconnect with the world. People with dementia aren't the only beneficiaries. Studies have shown that expressing themselves through art can help people with depression, anxiety, or cancer, too. And doing so has been linked to improved memory, reasoning, and resilience in healthy older people.
Recent Articles

An action plan to fight unhealthy inflammation

How to treat spider bites and when you need to see your doctor

Gratitude enhances health, brings happiness — and may even lengthen lives

Skin care for aging skin: Minimizing age spots, wrinkles, and undereye bags

Medicare versus Medicaid: Key differences

Prostate cancer: Short-course radiation as effective as longer-term treatments

Lost a tooth? What to know about dental implants

Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Evidence-based uses and unproven claims

Gatorade. Liquid IV. Do you need extra electrolytes?

Sexual violence can cast a long shadow on health
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up