How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond

Zinc: What it does for the body, and the best food sources

Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do
Pregnancy Archive
Articles
Postpartum anxiety is invisible, but common and treatable
It's not unusual for women to feel down or depressed after giving birth, but if the feelings persist or become debilitating, it's cause for concern. Many of the symptoms overlap between postpartum depression and postpartum anxiety, but some women do not respond as well to some treatments for depression, so it's important to establish the correct diagnosis.
How can you manage anxiety during pregnancy?
During pregnancy it's completely normal to experience a certain amount of anxiety about the baby, giving birth, and becoming a new parent. But for some women this worry takes over their thoughts and becomes debilitating. There are treatments available that may or may not involve medication, depending on the individual situation.
Common questions about medical cannabis
Pregnancy problems may predict heart health decades later
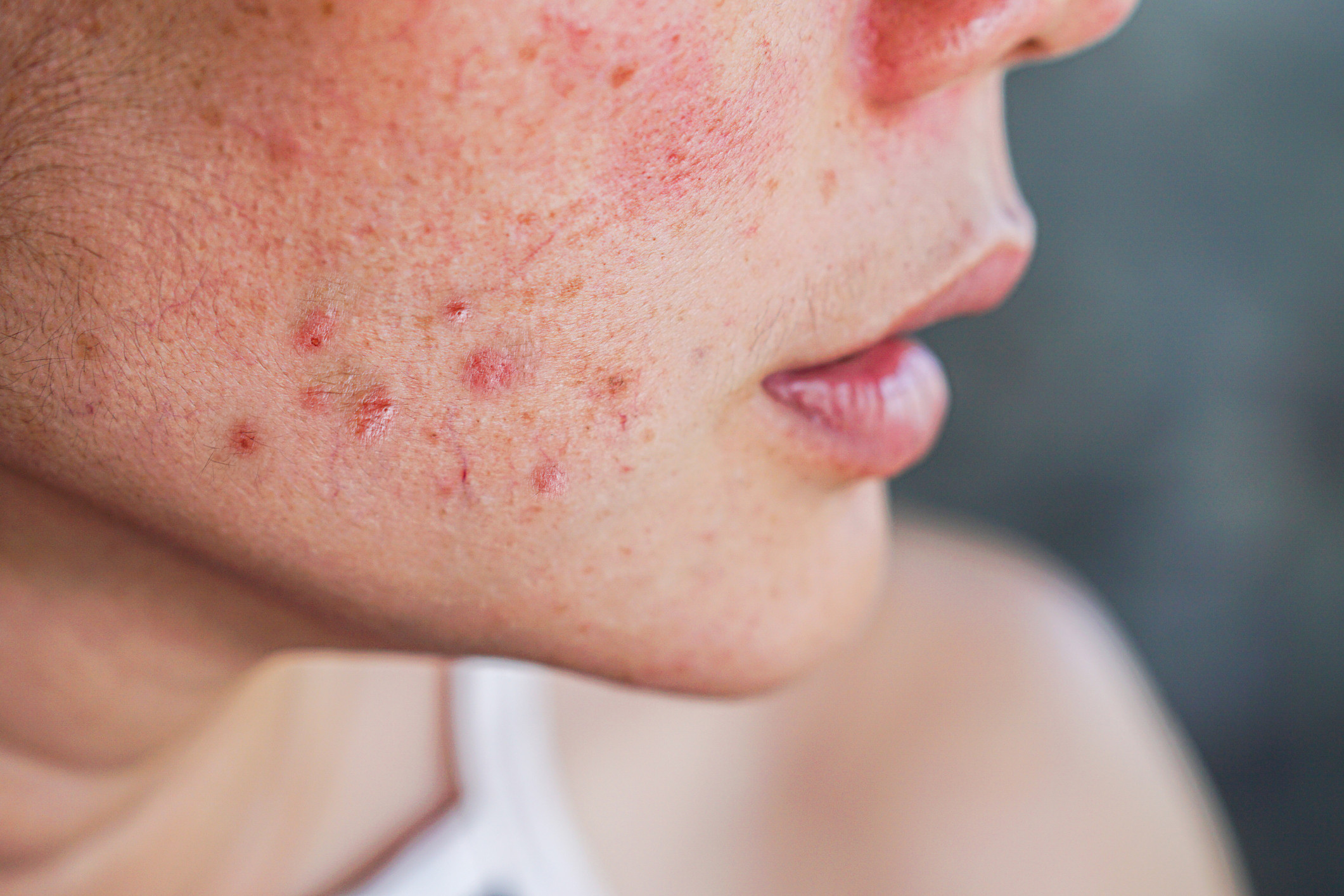
Polycystic ovary syndrome and the skin
Polycystic ovary syndrome is the most common cause of infertility in women. In many cases, women with PCOS have skin and hair issues such as acne, hair loss, or excessive hair growth in places where they normally do not have hair. Treatment options vary depending on the symptoms and each woman’s preferences.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome and the skin
Polycystic ovary syndrome is the most common cause of infertility in women. In many cases, women with PCOS have skin and hair issues such as acne, hair loss, or excessive hair growth in places where they normally do not have hair. Treatment options vary depending on the symptoms and each woman's preferences.
Does cannabis use impede conception?
Research we're watching
Women who use marijuana may have more difficulty getting pregnant than women who don't, according to a study published online Jan. 11, 2021, by the journal Human Reproduction.
The study looked at 1,200 women who were trying to conceive after experiencing either one or two miscarriages. The researchers followed the women for six monthly cycles and tracked those who became pregnant for the duration of their pregnancy. Those who reported using marijuana or hashish in the past 12 months or whose urine samples showed evidence of cannabis were 40% less likely to get pregnant during each monthly cycle than those who didn't use cannabis. Only 42% of the cannabis users became pregnant during the study period, compared with 66% of non-users. There did not, however, appear to be any difference in miscarriage rate between users and non-users. The study authors said that further research is needed to confirm the results.
Baby’s early arrival may hint at future heart problems for mom
Preterm birth joins other pregnancy-related conditions as potential heart risk factors.
Image: © metinkiyak/Getty Images
Preterm birth has long been known to bring health risks for the baby, but it may also bring risks for the mother. A study in the June issue of Hypertension shows that women who gave birth to a baby before 37 weeks of pregnancy were more likely to experience rising blood pressures later on compared to women who delivered closer to term. If they had this pattern, they were also more likely to show signs of coronary artery disease, which is associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Because of the unique demands that pregnancy places on a woman's body, it may serve as a stress test for the female heart, says Dr. JoAnn E. Manson, the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women's Health at Harvard Medical School. In the May issue, we talked about how other pregnancy-related conditions — gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia (a type of pregnancy-induced high blood pressure), and other pregnancy-related hypertensive disorders — can raise a woman's risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Preterm birth should now join that list, says Dr. Manson.
Birth control and high blood pressure: Which methods are safe for you?
Doctors typically recommend that women who have high blood pressure avoid using birth control that contains estrogen to avoid raising risks for a stroke or heart attack. According to a clinical update, this recommendation may be changing for some women with high blood pressure.
Pregnant and worried about the new coronavirus?

How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond

Zinc: What it does for the body, and the best food sources

Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up