Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Skin and Hair Archive
Articles
Inspect your nails for melanoma
You don't say? Hair today, gone tomorrow
Can a daily scoop of collagen powder really improve your skin?
Shaking off shingles
Shingles is a painful neurological condition that is more likely to attack as people age. Left untreated, it can increase risk for chronic pain, blindness, and other long-term health problems.
Shedding your skin
Chemical peels can help improve your skin, if you choose the right product and follow safety instructions.
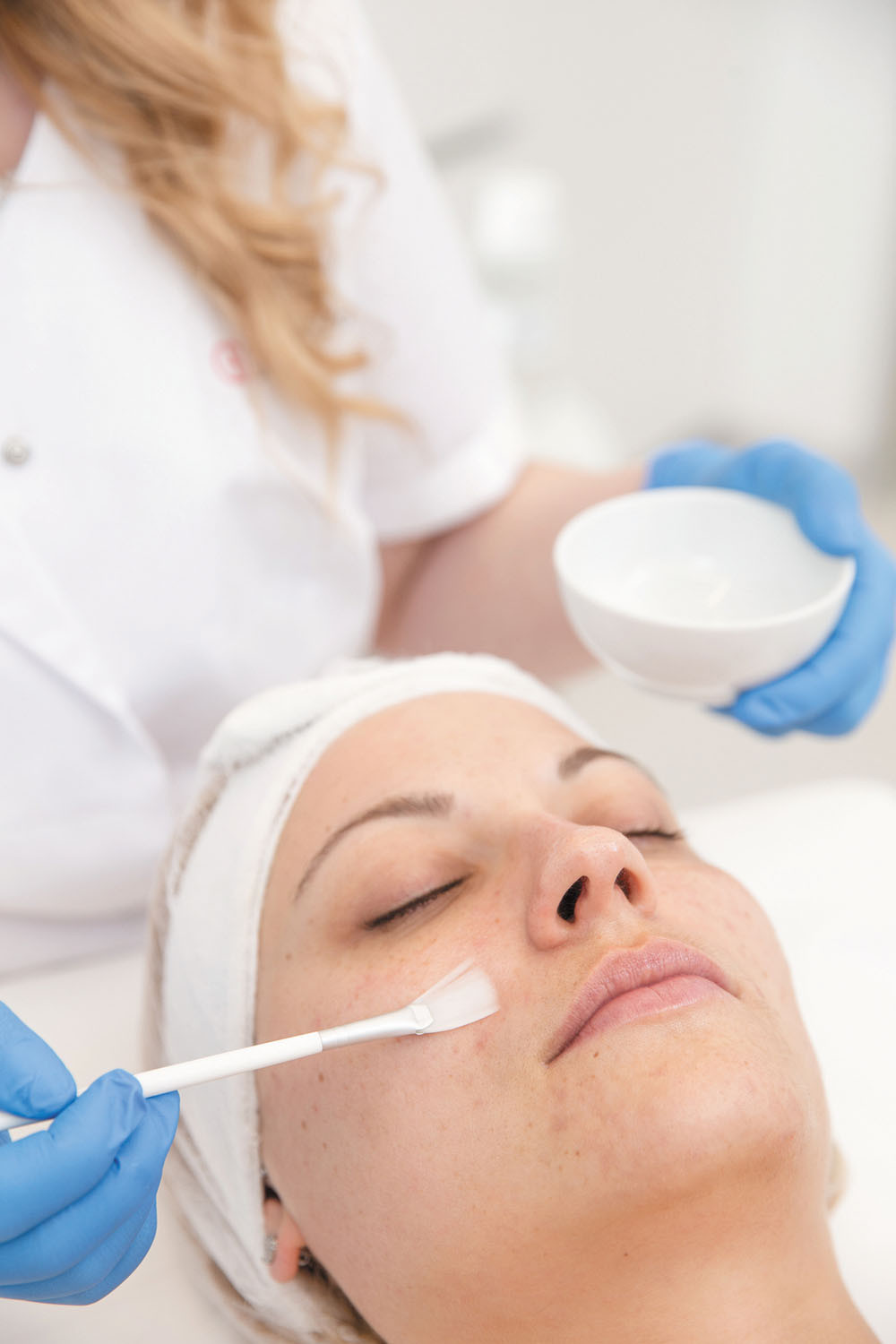
As you age, your skin changes, and not always in a good way. Some of the most common problems are caused by sun damage, including dark spots, rough texture, fine lines, and wrinkles. Chemical peels, which use a chemical solution to remove the top layers of the skin, are billed as one way to target these changes and improve the skin. Peels can be done at home, in a medical spa, or at a dermatologist's office. But the question is, are they really effective or good for your skin?
Dr. Hye Jin "Leah" Chung, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at Harvard Medical School, says yes, chemical peels can help your skin. But that endorsement comes with a caveat, she says. "They are beneficial as long as you use the right agent and the right technique," says Dr. Chung. Used incorrectly, chemical peels can be harmful and even cause burns or pigment changes.
Here comes the sun
With summer approaching, you need to be more attentive about sun protection.
Men have many skin challenges as they age. They develop wrinkles, lines, spots, and discoloration. Older men also are at greater risk for the two most common skin cancers: basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Without adequate sun protection, these conditions can become more frequent and severe.
Should I get a COVID-19 vaccine if I've had dermal fillers?
In rare cases, people who have had cosmetic dermal fillers experience swelling after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine, but this shouldn't stop people with fillers from being vaccinated.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome and the skin
Polycystic ovary syndrome is the most common cause of infertility in women. In many cases, women with PCOS have skin and hair issues such as acne, hair loss, or excessive hair growth in places where they normally do not have hair. Treatment options vary depending on the symptoms and each woman's preferences.

Driving with arthritis pain: Stay comfortable — and safe — behind the wheel

Daily cup of coffee may prevent afib recurrence

Gene-editing therapy lowers harmful blood fats in early study

What is EMDR therapy, and who can it help?

GLP-1 drugs versus bariatric surgery for treating obesity

Two dumbbells, three exercises, and 10 minutes

Easing the emotional burden of IBS

Modify your push-ups to meet your fitness level

What is long QT syndrome?

Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up