Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down
Staying Healthy Archive
Articles
Exercise-free activities that work your muscles and heart
Dancing, playing sports, and even cleaning your house can give you a nontraditional workout that helps maintain good health.
Image: Jon Feingersh/Thinkstock
Exercising is supposed to be a regular part of your daily health maintenance. That can be a problem if you don't have the motivation to get your heart pumping; you raise your risk for weight gain, chronic disease, and an earlier death.
Fortunately, you can get plenty of effective exercise by engaging in recreational or household activities that work your heart and muscles. "There's a real reward in doing an activity you enjoy, such as swimming or playing with your grandchildren. You get a workout, but it doesn't seem like you're exercising, and you may be more willing to keep doing that activity every day because it's fun," says Dawn Rogers, a physical therapist at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
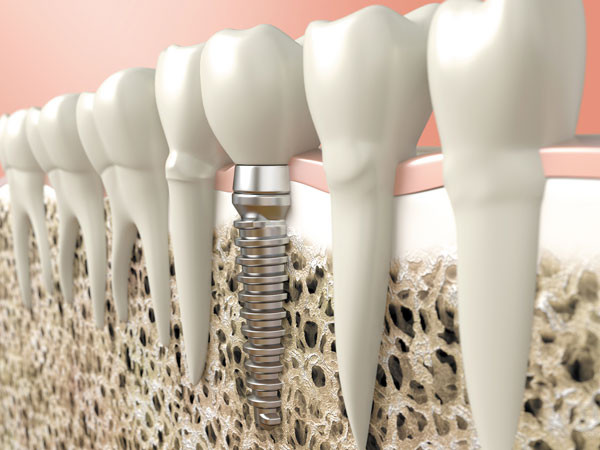
Dental implant reality check
Are these advances in dental health right for you?
Image: GuidoVrola/Thinkstock
Tooth decay, gum disease, and injury to the mouth can all lead to the loss of one or more teeth. The standard solution usually involves removable dentures or a fixed bridge. A newer option, dental implants, is also gaining popularity. "Implants can significantly improve your quality of life," says Dr. German Gallucci, department chair of restorative dentistry at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine.
About implants
Uses and benefits
In older adults, implants are typically used to replace one or two missing teeth (but not a mouthful). "Before implants, the only option we had was a bridge. With the implant, you can independently restore the tooth. That's a significant improvement in our therapy, to the point that we have reduced the number of bridges we do nowadays," says Dr. Gallucci.
Implants are also used to anchor a bridge or dentures. "Without implants, dentures move while you eat or speak, which makes it difficult to do either. But when you clip the denture onto an implant, it stays in place and functions normally," says Dr. Gallucci. He says supporting dentures or bridges may require two or more implants.
Requirements
Considerations
There are few downsides to getting implants. One is cost. "The range varies from state to state. It could be between $2,000 and $6,000 for one tooth and crown. But that's comparable to a bridge," says Dr. Gallucci.
Some insurance plans cover implants, especially for a missing tooth. Medicare does not pay for implants.
Another drawback: the time involved in healing. But the benefits, says Dr. Gallucci, can be worth it.
If you're interested in pursuing implants, he recommends getting several opinions. You can start by making an appointment with either a dentist who's surgically trained to place implants and has years of experience, or a prosthodontist—an expert in tooth restoration and replacement.
What to eat when your teeth and gums hurtIt's common after oral surgery to have some pain for a day or two, or even longer. This may mean that you have to be especially mindful of what you eat and drink. Sensitivity to hot and cold items is typical. But even the act of chewing can be uncomfortable. What's best to eat? "Avoid crunchy and sticky foods and stick to a soft diet," says Dr. German Gallucci, a restorative dentistry expert at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine. "Go with soups, pastas, yogurt, and even baby food." He advises avoiding the side of your mouth that's been operated on, and eating only small bites of food that keep your teeth from making forceful contact. Other tips: Avoid anything very hot on the first day after surgery, as heat can increase the risk of bleeding; drink a lot of fluid, at least five or six cups per day; and baby yourself. "Give your mouth a chance to heal," he says. |
More evidence that a healthy lifestyle might help prevent cancer
It appears that four healthy habits—getting 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, maintaining a body mass index between 18.5 and 27.5, no smoking, and drinking only in moderation—may prevent many cancer cases and death in white people.
Will the food industry ease up on salt?
On June 1, 2016, the FDA proposed voluntary guidelines for short- and long-term goals to cut sodium in commercially processed and prepared food.
Strategies for taking medications
Doctors may prescribe medications in hopes of helping a patient, but statistics show that at least half of all patients do not follow through with the treatment. Dr. Robert Schmerling explains why some people are choosing to skip taking medications and the possible results of not taking them.
Your blood work, on the edge of normal
What to do when routine test results are at the high or low end of the acceptable range.
Catching early changes in blood work may help prevent chronic disease, such as diabetes.
Image: Ca-ssis/Thinkstock
As a smart medical consumer, you know it's important to look over the results of your routine blood work, even when the numbers are all within the normal range. But what if you notice that some results are at the high or low end of that range? Should you be concerned about this?
Understanding empty calories
When a food provides primarily calories, and little else of value to health, that food is sometimes described as having empty calories.
Is an underlying condition causing your fuzzy thinking?
The top five causes you may be overlooking.
Image: the-lightwriter/iStock
You know the feeling: you can't find a particular word, remember someone's name, or concentrate the way you once did. Is it just aging, or is something else to blame? "It's easy to underestimate how underlying conditions affect memory and thinking, and they are often overlooked," says Dr. Shreya Raj, a neuropsychiatrist with the Center for Brain/Mind Medicine at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
Common causes
What you should do
When trouble with concentration or memory interferes with your day, it's probably time to talk to your primary care doctor. Report any additional symptoms you may be having, such as fatigue, muscle weakness, sadness, daytime sleepiness, or anxiety. You might need some blood tests to check your thyroid hormones or B12 levels (neither test is ordered routinely), or a sleep test if you have sleep apnea symptoms.
Often, treating an underlying condition can restore your clarity of thinking. "When we treat depression or sleep apnea, for example, we see a sudden improvement in memory and focus," says Dr. Raj. "And if a medication side effect is the problem, changing the dose or type of drug may resolve the problem."
If treating an underlying condition doesn't sharpen thinking skills, your doctor may refer you to a neuropsychologist for formal tests of your thinking ability, particularly signs of dementia. Most of the time, however, people with fuzzy thinking do not have dementia.
Fuzz bustersWhen you're struggling with fuzzy thinking, lifestyle changes like these can bring more clarity. Get more sleep. Aim for seven to eight hours of sleep per night. "Older adults to tend to sleep less, but if you're getting too little sleep, you won't think as sharply as you could," says Dr. Shreya Raj. Boost your Z's by going to sleep and waking at the same time each day, and avoiding caffeine, particularly after noon. Exercise more. Try to get 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week, such as brisk walking. You'll get more sleep and boost blood flow to the brain. Many studies have shown that aerobic exercise in particular improves thinking skills. Change your diet. "Not eating healthfully makes you more sluggish, even in thinking. Studies have shown the Mediterranean diet may improve cognitive function," says Dr. Raj. The diet includes fresh vegetables and fruits; whole grains; olive oil; nuts; legumes; fish; moderate amounts of poultry, eggs, and dairy; moderate amounts of red wine; and red meat only sparingly. Image: JackF/Thinkstock |
Try the hot trend in whole grains
Ancient grains have become the darlings of the culinary world, and they're healthy, too.
Image: marejuliasz/Thinkstock
In recent years, whole wheat has gotten all the glory when it comes to adding grains to your diet. But today's superstars are the staples used long before wheat took center stage. They're called ancient grains.
"Modern wheat, rice, and corn have been processed through hybridization or genetic modification. Ancient grains have not; they've been grown the same way for centuries," says Debbie Krivitsky, a registered dietitian at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.
Botox injections get another nod for treating migraine headaches
In its 2016 guidelines, the American Academy of Neurology recommended the use of onabotulinumtoxin A (Botox) injections as a way to help reduce the frequency of chronic migraines.

Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up