Counting steps is good — is combining steps and heart rate better?

Appendix pain: Could it be appendicitis?

Can saw palmetto treat an enlarged prostate?

How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond

Zinc: What it does for the body, and the best food sources

Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?
Staying Healthy Archive
Articles
Immune boosts or busts? From IV drips and detoxes to superfoods
Ads for products that promise to supercharge the body's immune system make claims that sound too good to be true. But do these products actually work?
Can you feel younger than your age?
Research has found that people with more positive attitudes about growing old tend to live longer than those with negative thoughts about aging. They also have a lower risk for diabetes, stroke, cancer, and heart disease and better cognitive functioning. People can maintain a healthy mindset about aging by adopting certain lifestyle habits, such as reducing anxiety, finding purpose in life, seeking challenges, socializing more, and rejecting negative stereotypes about aging.
Exercise may counteract inherited risk for diabetes
Getting regular exercise can help fend off diabetes, even in people with a genetic propensity for the disease, according to a 2023 study.
Seeing clogged arteries may inspire healthier habits
If people see evidence of plaque buildup inside their arteries, it may motivate them to take better care of their heart health, according to a 2023 study.
Medication-taking made easier
About half the time, people alter how much, how often, or how long they take a prescribed medication, or they don't take it at all. This phenomenon, called medication nonadherence, can gravely threaten people's health, and is linked to about 125,000 deaths annually. People might not be able to comply with their drug regimen if they feel they take too many drugs, they don't like the side effects, the prescriptions cost too much, or they have memory problems or depression. Doctors should review medication lists and remove what patients no longer need.
Eating junk food may affect deep sleep
A new study found that eating an unhealthy diet high in processed food can affect people's deep sleep, the stage when the pituitary gland in the brain releases hormones to build and repair muscles and bones as well help boost cognitive function and memory.
Is it okay to take multivitamins?
The general consensus is that healthy people who eat right need a vitamin or mineral supplement only if they have a diagnosed vitamin or mineral deficiency. Still, multivitamins may provide a safety net to fill dietary nutrition gaps even for people who mostly eat healthy. Studies have shown that taking multivitamins as prescribed usually doesn't cause any serious issues, and many over-the-counter brands are relatively inexpensive. Some people also view taking a daily multivitamin as another way to support a healthy lifestyle.
Rising up from a fall
Older adults need to safely be able to sit and rise from the ground whether kneeling in the garden, looking for something under the bed, or playing on the floor with the grandkids. This movement is also helpful when getting up after a fall. Three exercises that can help older adults with daily up-and-down mobility are kneel-to-stand, crawling, and sit-to-stand.
How to avoid this common pickleball injury
Pickleball elbow is a type of tendinitis called lateral epicondylitis. The injury can result from gripping a pickleball paddle tightly for long periods or repeatedly twisting and turning the wrist while preparing to hit the ball. To avoid pickleball elbow, doctors recommend that players improve their muscle strength, use a paddle with the right grip size, build time on the court gradually, warm up their muscles before playing, stretch muscles afterward, ice their elbows after playing, and get guidance to hone their pickleball technique.
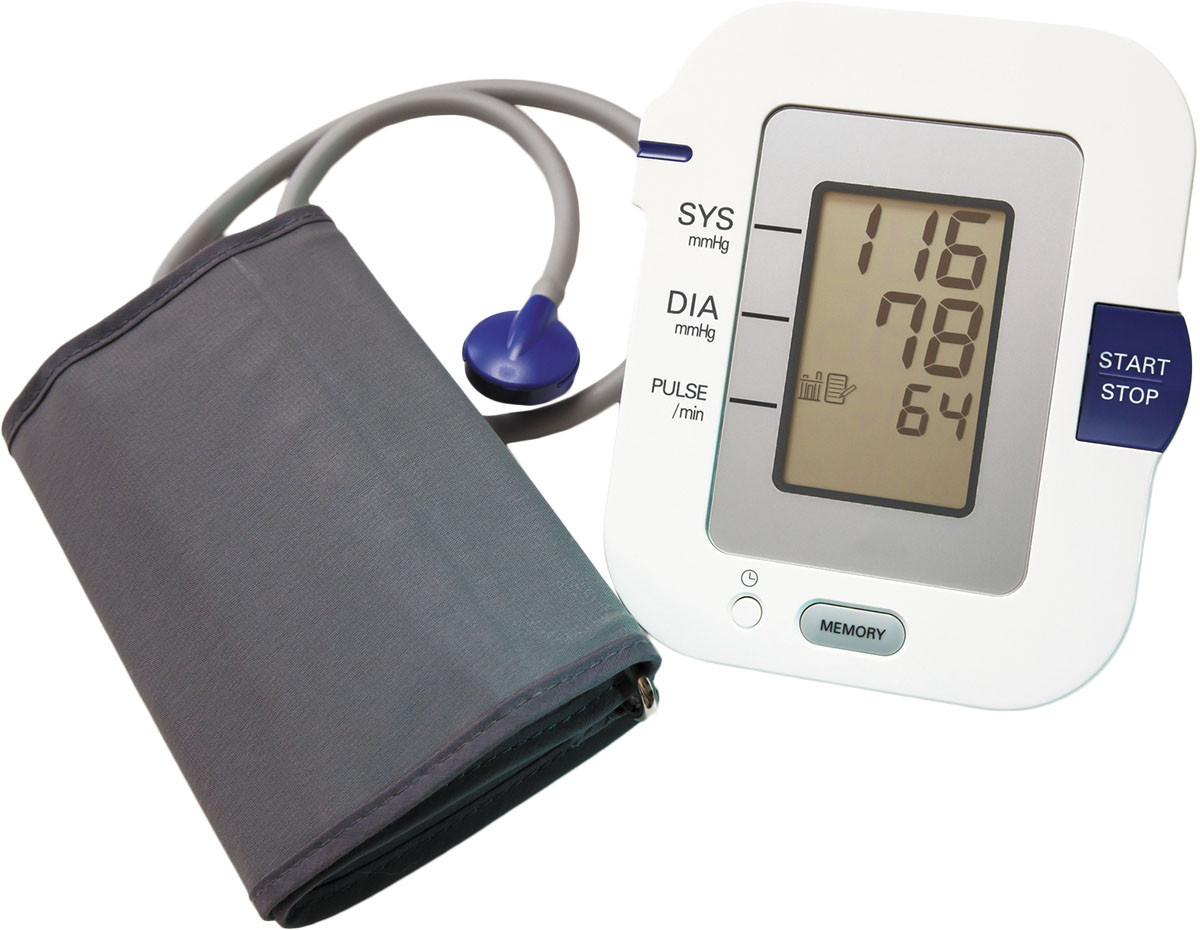
Is your home blood pressure monitor accurate?
Many home blood pressure monitors are not validated for accuracy, which means there's no way to know if information they provide is correct. Relying on inaccurate measurements can affect decisions people make about medical treatment. Fortunately, reliable organizations have developed lists of blood pressure monitors that have demonstrated clinical accuracy. If a blood pressure monitor isn't listed, it's probably not validated.

Counting steps is good — is combining steps and heart rate better?

Appendix pain: Could it be appendicitis?

Can saw palmetto treat an enlarged prostate?

How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond

Zinc: What it does for the body, and the best food sources

Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up