How we make memories

Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve
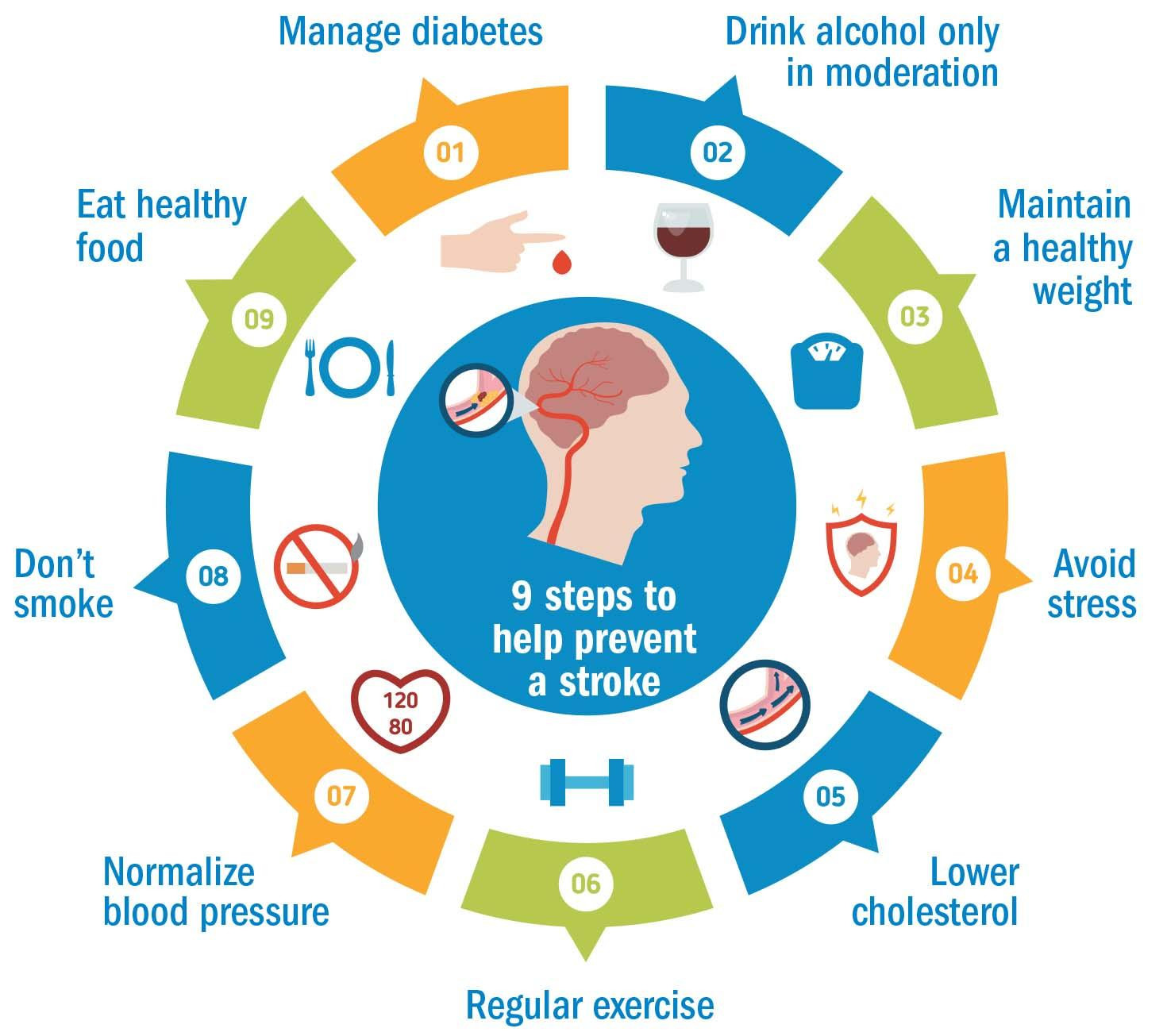
Stroke Archive
Articles
How good is your cardiometabolic health - and what is that, anyway?
An analysis shows less than 7% of adults in the US meet the criteria for optimal cardiometabolic health. Taking small steps to help control and improve key risk factors can reduce the odds of a heart attack or stroke.
Does everyone benefit from cutting saturated fat in their diet?
A review of 17 studies found that for people at high risk of heart disease, cutting down on saturated fats may have lowered their risk of major cardiac events over the next five years, but people at lower risk did not see similar benefits.
New thinking about plaque in arteries that feed the brain
Carotid artery stenosis, which happens when fatty plaque accumulates in neck arteries that supply the brain, leaves people vulnerable to a stroke. Intensive drug therapy may forestall the need for invasive procedures to treat this problem.
Stroke survivors may benefit from very low LDL levels
For stroke survivors, reaching a very low LDL (bad) cholesterol level may reduce their risk of future strokes and other cardiovascular problems, according to a 2025 study.
Reducing your stroke risk after a ministroke
A transient ischemic attack (TIA), or ministroke, is a serious warning sign for future stroke, especially in the first 48 hours. Medications plus lifestyle changes-healthy eating, regular exercise, and blood pressure control-can significantly lower that risk.
Nighttime light exposure linked to heart disease
Higher exposure to light at night between 12:30 a.m. and 6 a.m. is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular problems including coronary artery disease, stroke, atrial fibrillation, heart attack, and heart failure.
Gum disease may increase the risk for stroke and cognitive decline
A 2025 study found that in brain MRI scans, people with any evidence of gum disease were more likely to have higher amounts of a marker for disease in the brain's small blood vessels, compared to people without gum disease.
Poor sleep raises risk of heart problems in menopausal women
A 2025 study identified poor sleep along with high blood pressure, nicotine use, and high blood sugar levels as particularly important factors increasing the long-term risk of heart problems for women in midlife.
Nearly everyone has at least one risk factor before a heart attack, heart failure, or stroke
A 2025 study suggests that more than 99% of people who have a first-time heart attack, stroke, or heart failure have at least one of four risk factors: unhealthy blood pressure, cholesterol, or blood sugar levels, or past or present smoking.
The heart attack and stroke emergency playbook
Everyone should learn what to do if a heart attack or stroke occurs, beyond calling 911. It helps to become familiar with heart attack and stroke symptoms, so they can be recognized. It's also important to speak with one's own doctor in advance, to find out if he or she advises taking an aspirin in one of those emergencies. Other precautions include keeping emergency contact and medication lists updated and handy, and talking about emergency plans with family and friends, especially one's health care proxy.

How we make memories

Aldosterone overload: An underappreciated contributor to high blood pressure

Can you retrain your brain to stop excessive drinking?

Beyond statins: New ways to lower LDL cholesterol

What is a cardioversion procedure?

For now, electric cars appear safe for people with implanted heart devices

Can you stop blood thinners after an ablation for atrial fibrillation?

Reversing prediabetes may slash heart disease risk by half

Waking up to urinate at night affects blood pressure

Finding and fixing a stiff, narrowed aortic valve
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up