Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down
Women's Health Archive
Articles
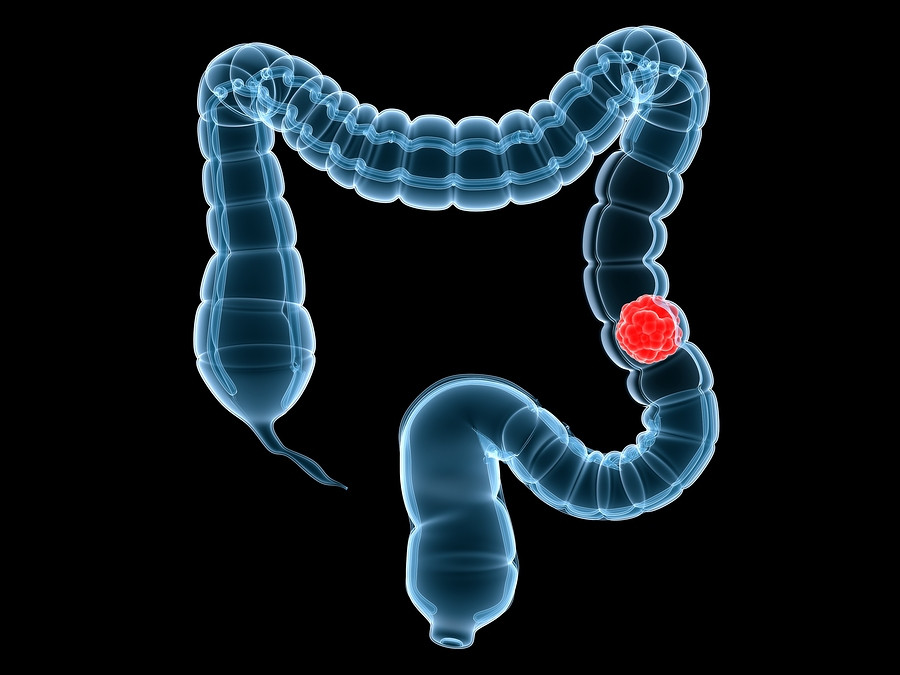
A new look at colon cancer screening
Don't be intimidated about screening tests. The latest guidelines suggest you can choose from multiple strategies.
Image: Bigstock
Colon cancer continues to be the country's second leading cause of cancer-related deaths and the third most common cancer in men, according to the CDC.
It almost always develops from precancerous polyps (abnormal growths). Screening tests, which are recommended for men ages 50 to 75, help find and sometimes aid removal of polyps before they become cancer. (Men older than 75 may still benefit, depending on their health.)
Easy ways to build better bones
Strength training, weight-bearing exercise, a healthy diet, and medication can help.
Image: Tatomm/iStock
An estimated 10 million people in the United States are coping with the brittle, fragile bones of osteoporosis—a disorder that causes severe bone loss. It's most common in women, and the risk is higher in those who are thin, age 50 or older, or of Caucasian or Asian descent. It also occurs in men, who make up about 20% of osteoporosis cases. The condition puts a person at a high risk for bone fractures, disability, loss of independence, and even death. That's why it's important to make your bones as strong as possible. "There are many ways to build bone mass, and the people who do tell us they feel stronger and more capable on their feet," says Rachel Wilson, a physical therapist at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
There isn't one magic way to build bone mass. It takes a number of the following strategies.
Staying active at “that time of the month”
The belief that women should avoid exercise or athletics during their menstrual periods, because it can affect performance or increase the risk of injury, is not necessarily true. Good training may reduce the risks of injury and enhance performance much more than trying to time exercise around one’s periods.
Join the healthy heart trend
The rates of heart disease have dropped over the past decade. How can you be part of this pattern?
Image: Photos.com/ Thinkstock
Heart disease continues to be the No. 1 cause of death among men, but there is some good news—fewer older adults have heart disease. A recent report from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found the rates for this condition among people age 60 and older have fallen from 19.5% to 14.9% in the past decade.
What caused this downward trend? And how can you follow?
You can protect yourself against superbugs
Some simple preventive measures can keep antibiotic-resistant bacteria at bay.
Image: hxdbzxy /Thinkstock
Although the Zika virus got more publicity throughout the summer, another—and even scarier-sounding—microbe also made headlines. Dubbed a new "superbug," strains of E. coli resistant to the antibiotic colistin were found in the United States. Colistin is a drug often used when others fail to control a bacterial infection. Fortunately, the bacteria weren't resistant to other antibiotics, which cleared the infections. "Although this particular case of antibiotic resistance may not be as dire as the media made it sound, in general these increasingly high-level resistances are an enormous problem," says Dr. Sarah Fortune, professor of immunology and infectious diseases at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Why superbugs are such a problem
Like other forms of life, bacteria are always evolving to become stronger and survive longer. One of the ways they increase their chances of survival is to acquire genes that help them resist threats—including natural enemies like viruses and man-made weapons like antibiotics. These genes can spring up within a bacterium through mutations and are passed down to subsequent generations of the microbe. In addition, they can be found on rings of DNA called plasmids, which can be transmitted to other types of bacteria, enabling the resistance to spread wider and faster. The E. coli strains discovered in 2016 raised concern because they carry the colistin-resistance gene on plasmids and thus have the potential to transfer the plasmids to bacteria that are already resistant to several other antibiotics.
Birth control right after having a baby: Why it’s important, why it should be covered
Many women may plan to start using birth control at their six-week postpartum checkup, but as many as 40% of women do not go to a follow-up appointment. The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists advocates for offering women the option of long-acting, implantable contraceptives in the period immediately following giving birth, before leaving the hospital. It’s safe, effective, and eliminates the need for an outpatient visit during a hectic time. Making postpartum contraception easily available and a covered benefit is essential to reduce unintended pregnancy and rapid, repeat pregnancy rates.
Would having stronger core muscles speed my recovery from abdominal surgery?
Strong core muscles and overall fitness are linked to shorter surgical recovery times.
Shunning osteoporosis treatment isn’t a wise decision for most women
Forgoing drugs that slow bone loss to avoid rare side effects can be the wrong decision for your hips and spine.
Image: wildpixel/Thinkstock
A front-page article in the June 1, 2016, edition of The New York Times carried this headline: "Fearing drugs' rare side effects, millions take their chances with osteoporosis." The article described a situation all too familiar to doctors. Women are declining prescriptions of bisphosphonates—drugs that slow the rate at which the body breaks down bone—or discontinuing the medications far earlier than recommended. In fact, according to a 2015 report in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, the rate of bisphosphonate use fell by half between 2008 and 2012. That article documented a wave of media coverage of scientific studies that reported two rare side effects—osteonecrosis (bone death) of the jaw and atypical fractures near the top of the femur (thigh-bone)—and suggested that the reports had kindled fears that had led women to abandon bisphosphonates.
"The perception of risk is so much greater than the actual risk," says Dr. Meryl LeBoff, director of the skeletal health and osteoporosis center at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. Compared with many other common diseases, we are fortunate that we have good therapies to reduce the risk of osteoporotic fractures by 70% at the spine and 40 to 50% at the hip. She points to statistics referenced in the New York Times article: for every 100,000 women taking a bisphosphonate, fewer than three will have osteonecrosis of the jaw and one will have an atypical femur fracture, but 2,000 will have avoided an osteoporotic fracture.
Why you should heed a ministroke
Transient ischemic attacks, or TIAs, can signal an impending stroke, but prompt care can minimize damage.
Image: FlairImages/Thinkstock
Have you ever experienced a brief episode when your body seemed to be a little off—your vision was blurry, your speech slightly slurred, or one side of your body felt weaker than the other? If so, you may have experienced a transient ischemic attack (TIA), says Dr. Natalia Rost, a neurologist at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital. She notes that many women may assume they have suffered a migraine and get back to life as usual once the episode has passed. In fact, a TIA is a serious medical issue and warrants getting immediate treatment.
Immediate treatment is key
Having a TIA is usually a sign that you may have already endured a few "silent strokes"—interruptions of blood flow to the brain—and may have accumulated some brain damage as a result, Dr. Rost says. However, getting prompt attention for a TIA can significantly reduce your chance of having a major stroke and incurring greater damage.
A team of French researchers reported in April 2016 that people who received care from a stroke specialist within 24 hours of a TIA had only a 4% risk of having a major stroke within the next three months, compared with the average risk of 12% to 20%. Recent studies also show that people who got prompt treatment from stroke specialists in the hospital or clinic were much more likely to get the appropriate follow-up treatments, including aspirin, blood thinners, and blood pressure medication. "Just as getting prompt treatment for chest pain minimizes damage from a heart attack, getting help for a TIA diminishes the effects on the brain," Dr. Rost says.
Yet studies have shown that women aren't as likely as men to get brain-sparing treatments. A 2013 study indicated that gender discrimination wasn't the problem; women were less likely than men to seek help within four hours of the start of symptoms, when clot-busting therapies are most effective. Women who sought help within four hours received the same treatment as men did.
Why white matter really matters
What you should do
Dr. Rost suggests doing everything you can to minimize white-matter damage—controlling your blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood glucose are important. So is a lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a healthy diet, and not smoking. "While it's important to get help for a TIA, it's better to avoid one altogether," Dr. Rost says.
Pessary and exercise relieve symptoms for women with pelvic floor prolapse
A pessary and pelvic floor exercises can improve symptoms of pelvic floor prolapse.

Respiratory health harms often follow flooding: Taking these steps can help

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up